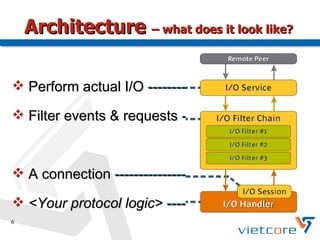
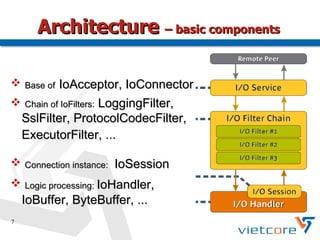
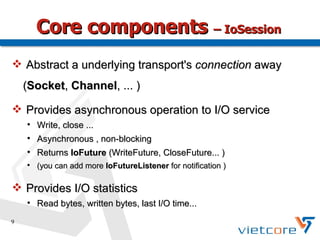
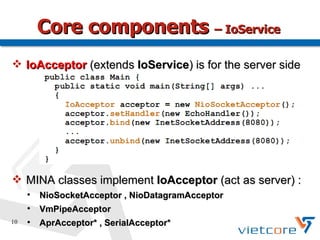
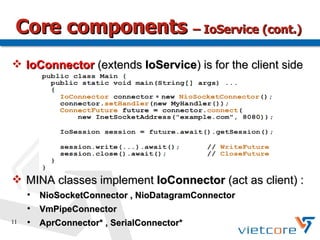
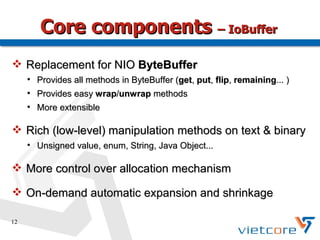
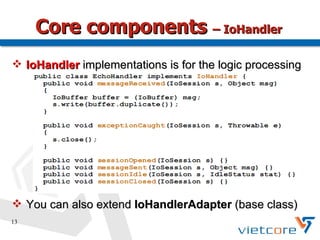
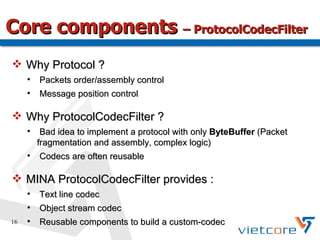
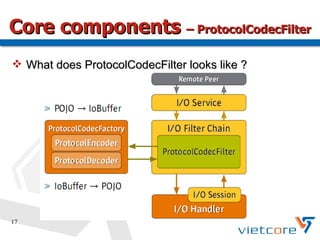
Apache MINA2 is a Java open-source network application framework that provides an asynchronous, non-blocking infrastructure for developing network applications. It features reusable and extensible components like IoSession for connections, IoService for servers/clients, IoFilters for cross-cutting concerns, and ProtocolCodecFilters for encoding network protocols. MINA supports various network protocols and data types and provides an elegant way to build scalable and manageable network applications.