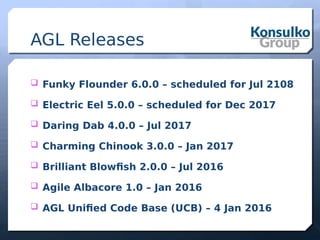
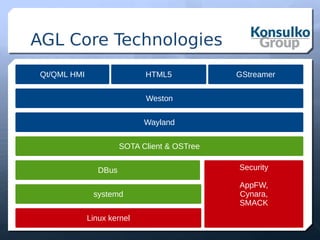
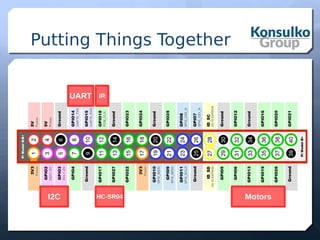
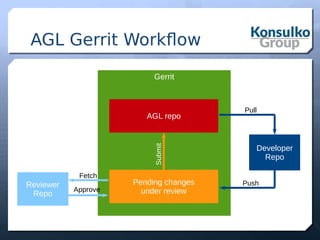
The document discusses building a remote control robot using Automotive Grade Linux (AGL), detailing the hardware requirements, software stack, and development tools. It outlines the features and benefits of AGL for IoT applications and provides step-by-step guidance for creating the robot, including motor control and sensor integration. The document concludes with insights on contributing to AGL and future developments in the project.