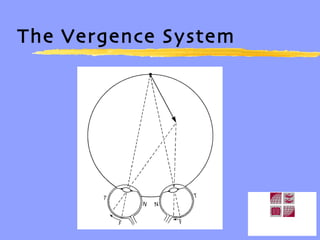
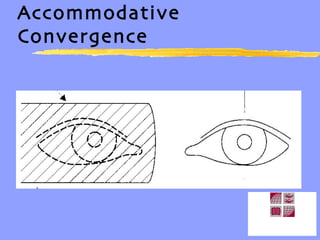
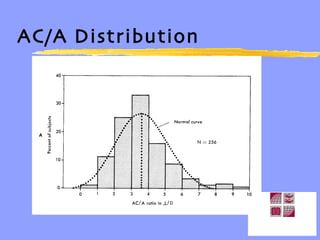
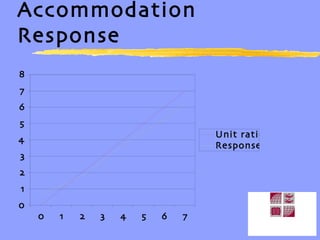
Vergence eye movements allow for the convergence and divergence of the eyes to change the angle formed by the visual axes. The vergence system includes voluntary and reflexive components. Reflex vergence is composed of tonic, accommodative, proximal, and fusional vergence responses. Accommodative convergence is the vergence response stimulated by accommodation. The AC/A ratio represents the relationship between accommodation and convergence. Maintaining the proper balance between all the components of the vergence system is important for managing vergence and binocular vision problems.