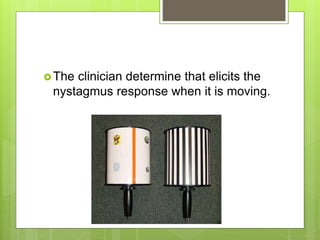
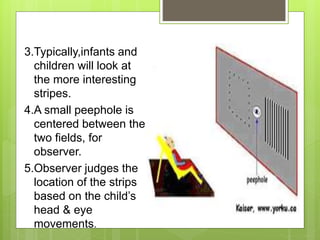
This document discusses methods of measuring visual acuity in infants. It describes that visual acuity improves rapidly in the first years of life and matures around 5-6 years old. Several tests are mentioned, including optokinetic nystagmus testing, preferential looking tests, visually evoked responses, Cardiff acuity card tests, and observation of fixation behavior. Normal visual development milestones from birth to age 5 are provided. The document gives details on different visual acuity tests used with infants, such as the optokinetic nystagmus test, preferential looking test, and Lea paddle test.