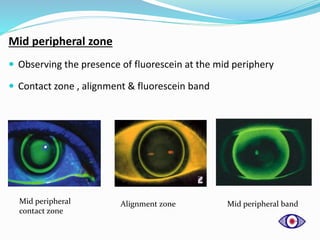
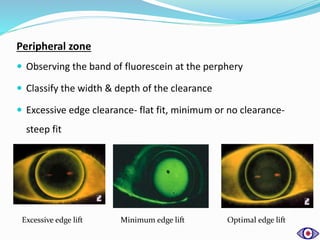
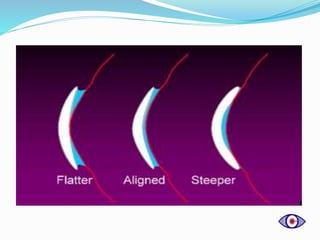
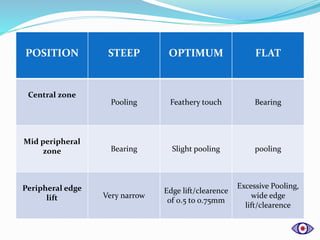
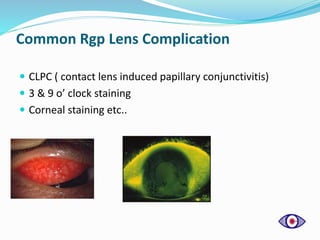
This document discusses rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses. It notes that RGP lenses are made of oxygen permeable materials and are better than soft lenses for vision, durability, correcting astigmatism, eye health, and ease of care. RGP lenses are recommended for conditions like keratoconus or high refractive errors. The fitting process involves screening patients, measuring the eye, trial fittings, and dynamic and static assessments. Proper care and maintenance of RGP lenses is also discussed.