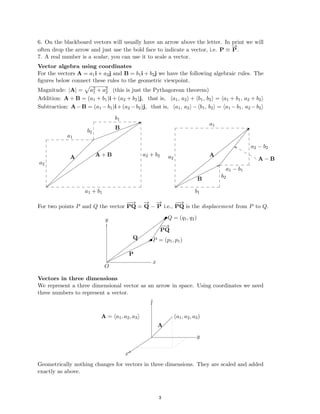
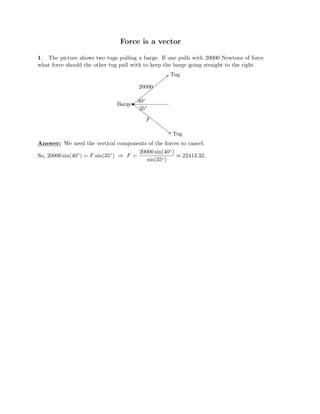
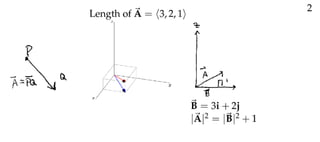
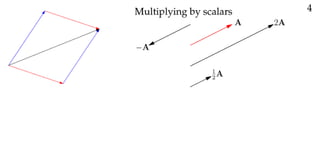
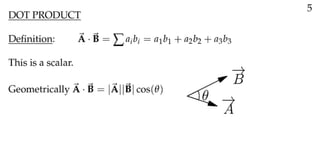
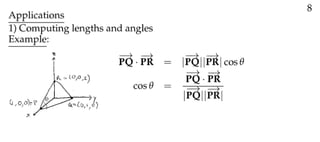
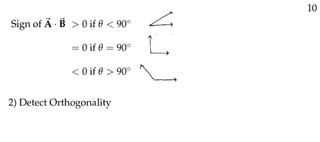
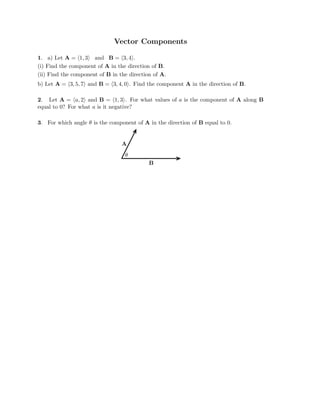
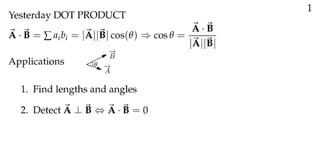
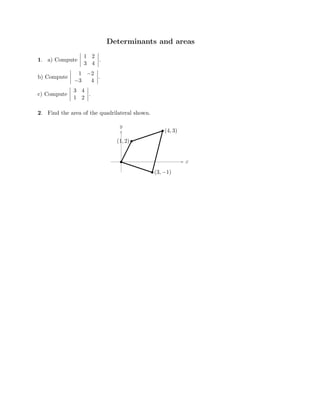
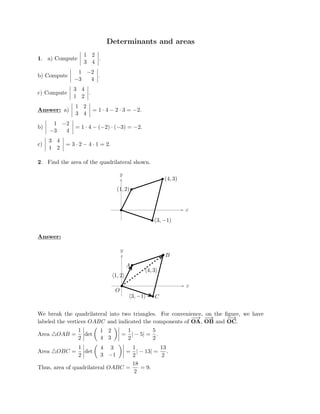
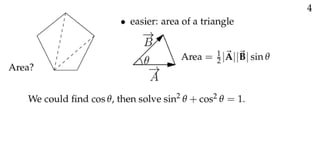
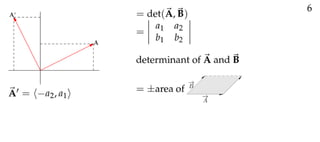
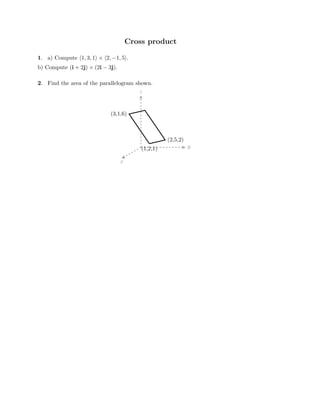
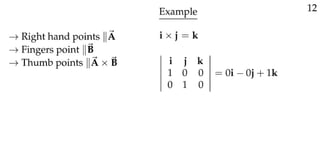
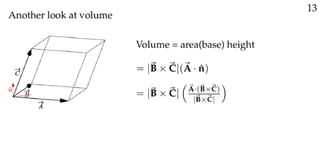
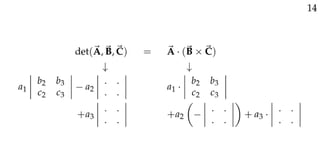
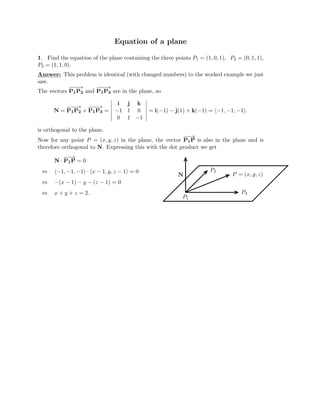
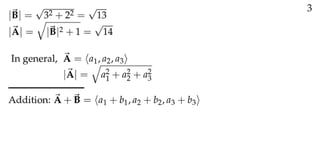The document defines vectors and discusses their geometric and algebraic representations. Geometrically, a vector has a magnitude and direction represented by an arrow. Algebraically, a vector in a plane can be represented by its coordinates (a1, a2) and in 3D space by coordinates (a1, a2, a3). Vectors can be added by placing them head to tail, subtracted by reversing one and adding, and scaled by a scalar number. The dot product of two vectors A and B yields a scalar value that geometrically equals the magnitudes of A and B multiplied by the cosine of the angle between them.