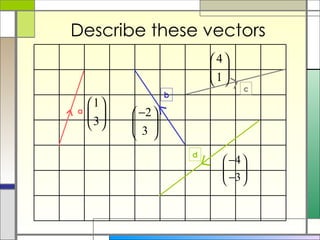
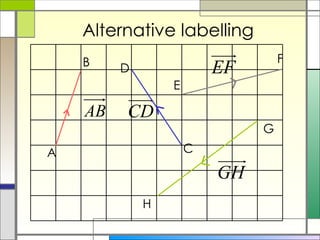
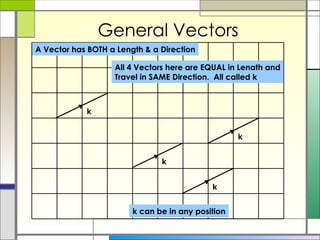
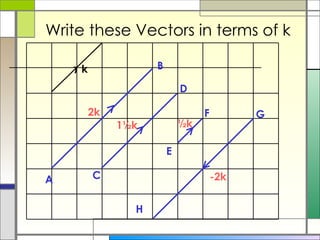
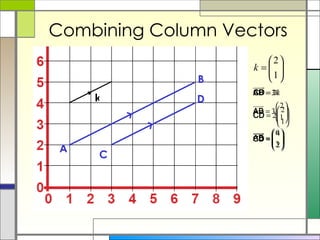
1) A vector describes both the direction and magnitude of motion of an object. Vectors can be represented as column vectors or general vectors.
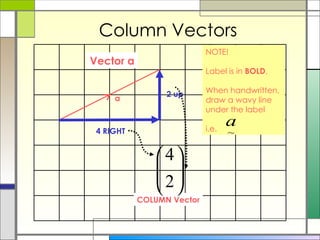
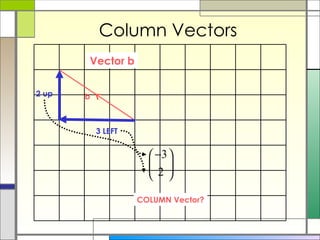
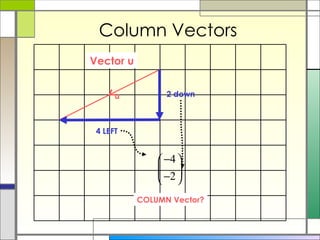
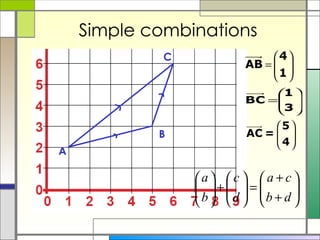
2) Column vectors are labeled with bold letters and a wavy line underneath. They represent vertical and horizontal components. General vectors can be positioned anywhere and represent motion using a single length and direction.
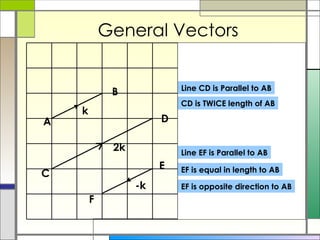
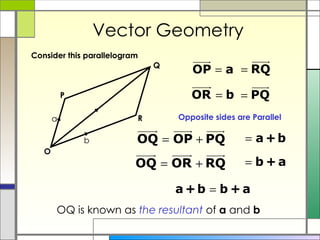
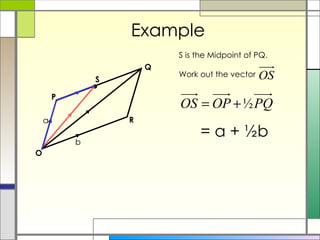
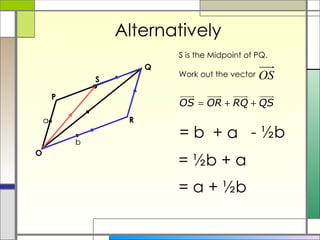
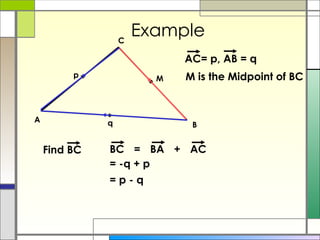
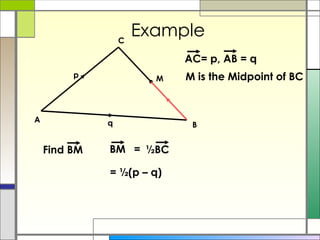
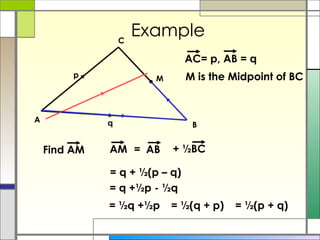
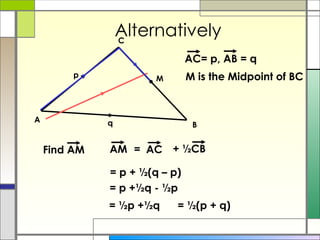
3) The resultant of two vectors is the same no matter the route taken to get there. It can be used to find unknown vectors in geometric figures.