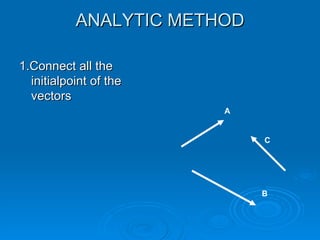
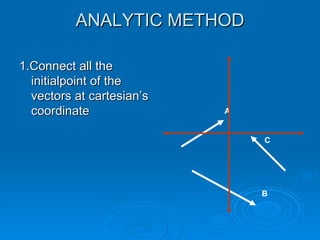
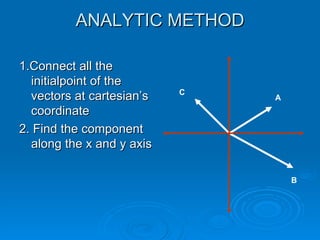
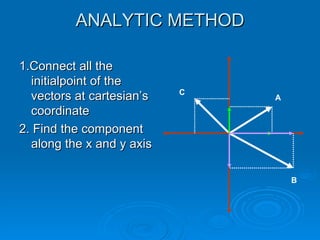
The document describes several methods for finding the vector sum (resultant) of two or more vectors, including:
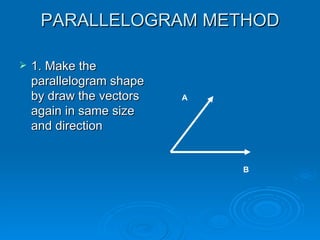
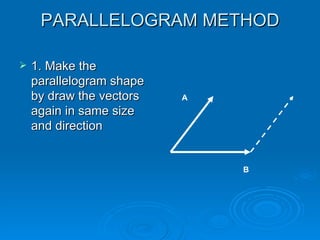
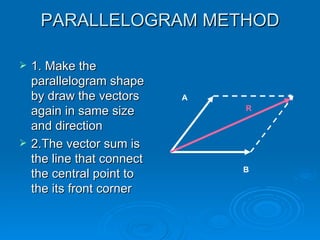
1. The parallelogram method draws the vectors to form a parallelogram, with the resultant being the diagonal.
2. The cosine method uses a formula involving the magnitudes of the vectors and the angle between them.
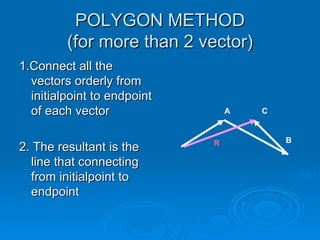
3. The polygon method connects the vectors tip to tail to form a polygon, with the resultant connecting the initial and final points.
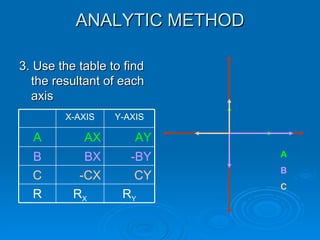
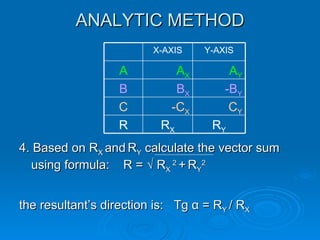
4. The analytic method resolves the vectors into their x and y components, sums the respective components, and determines the resultant's magnitude and direction from the sums and a formula.