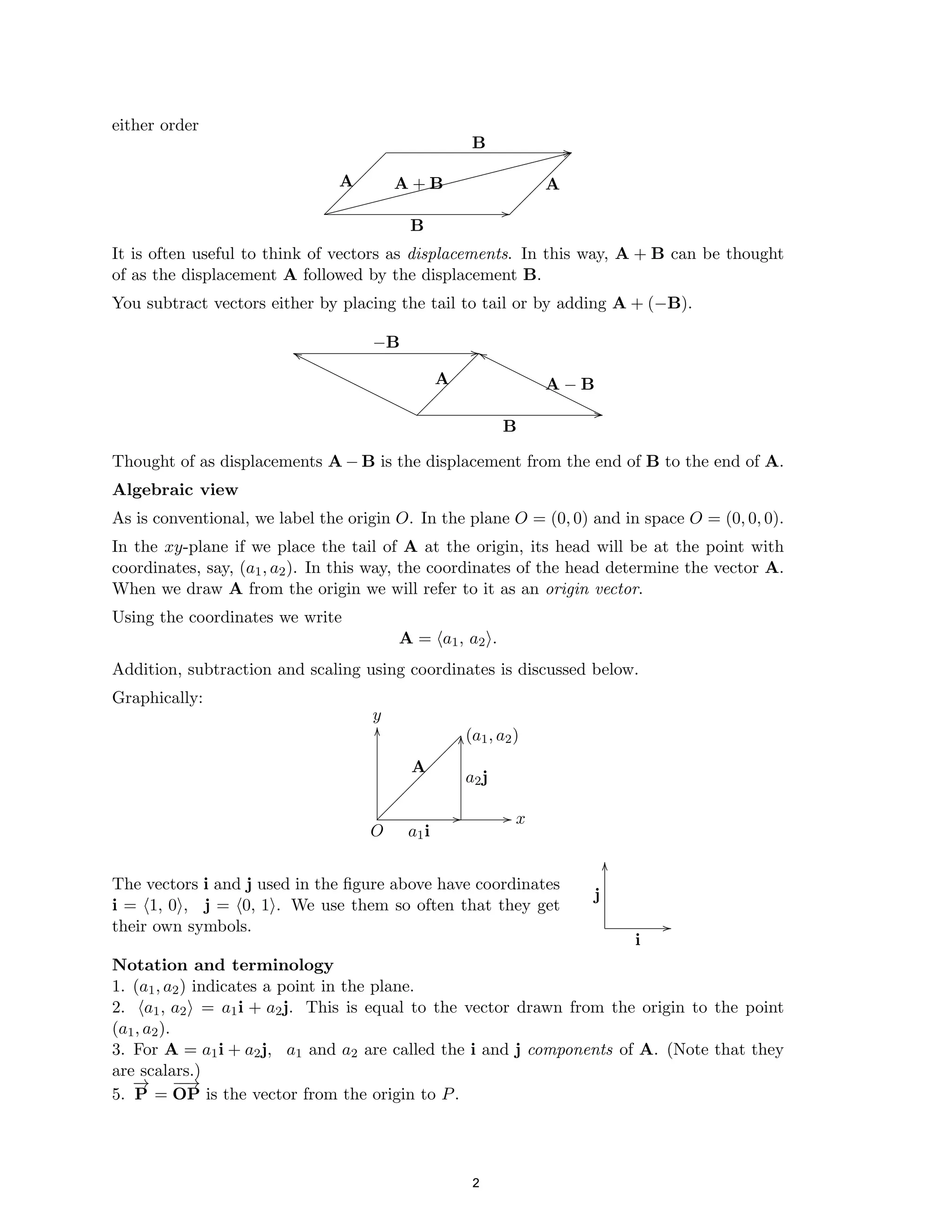
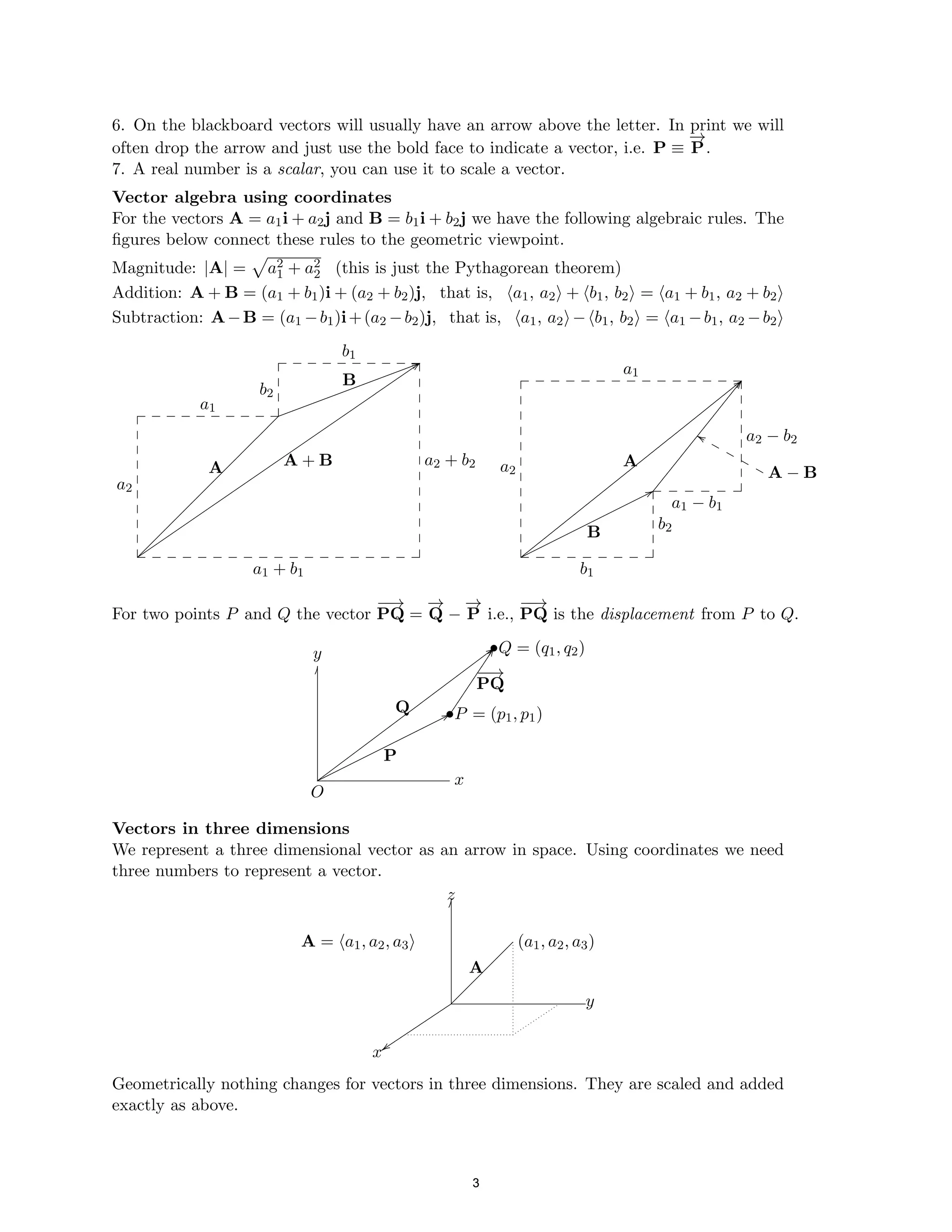
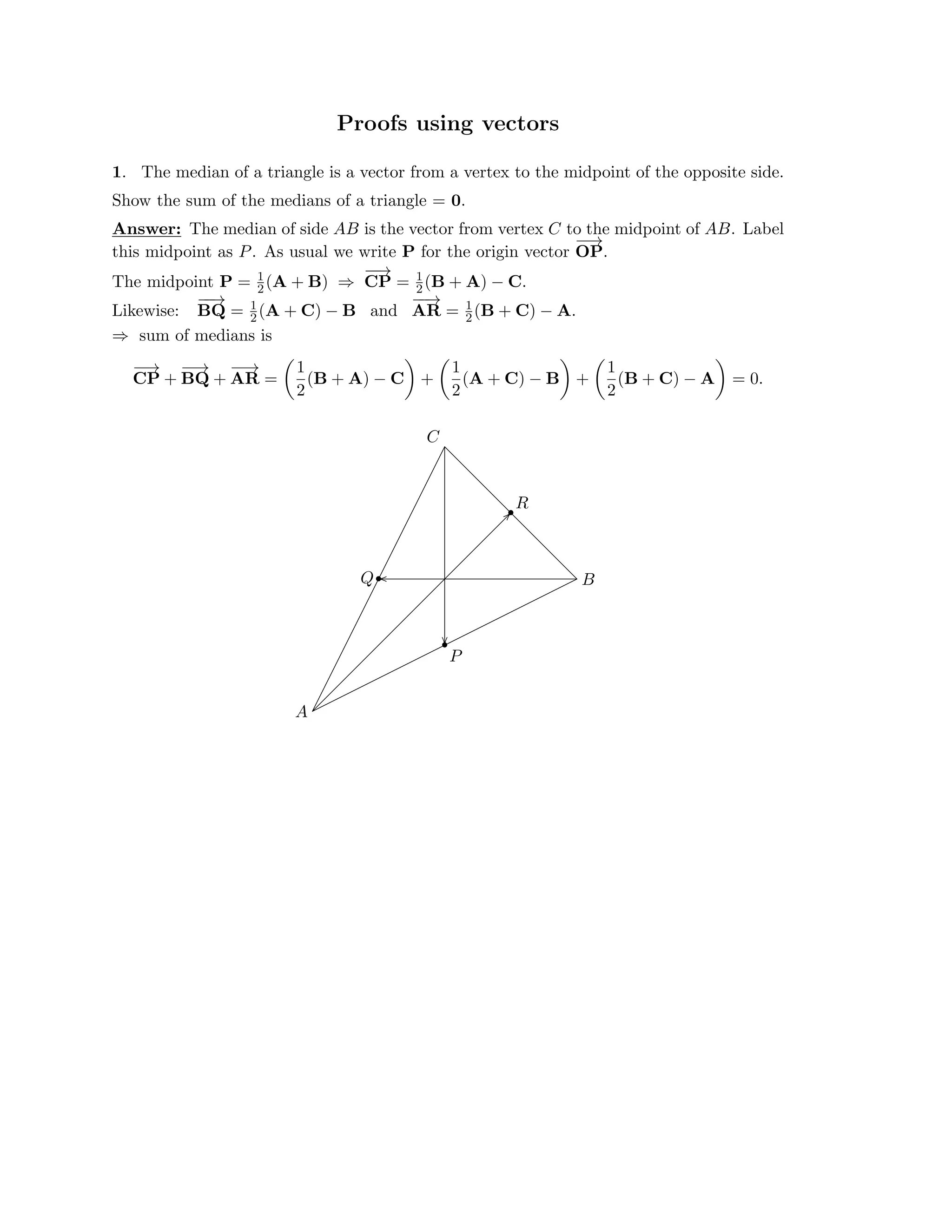
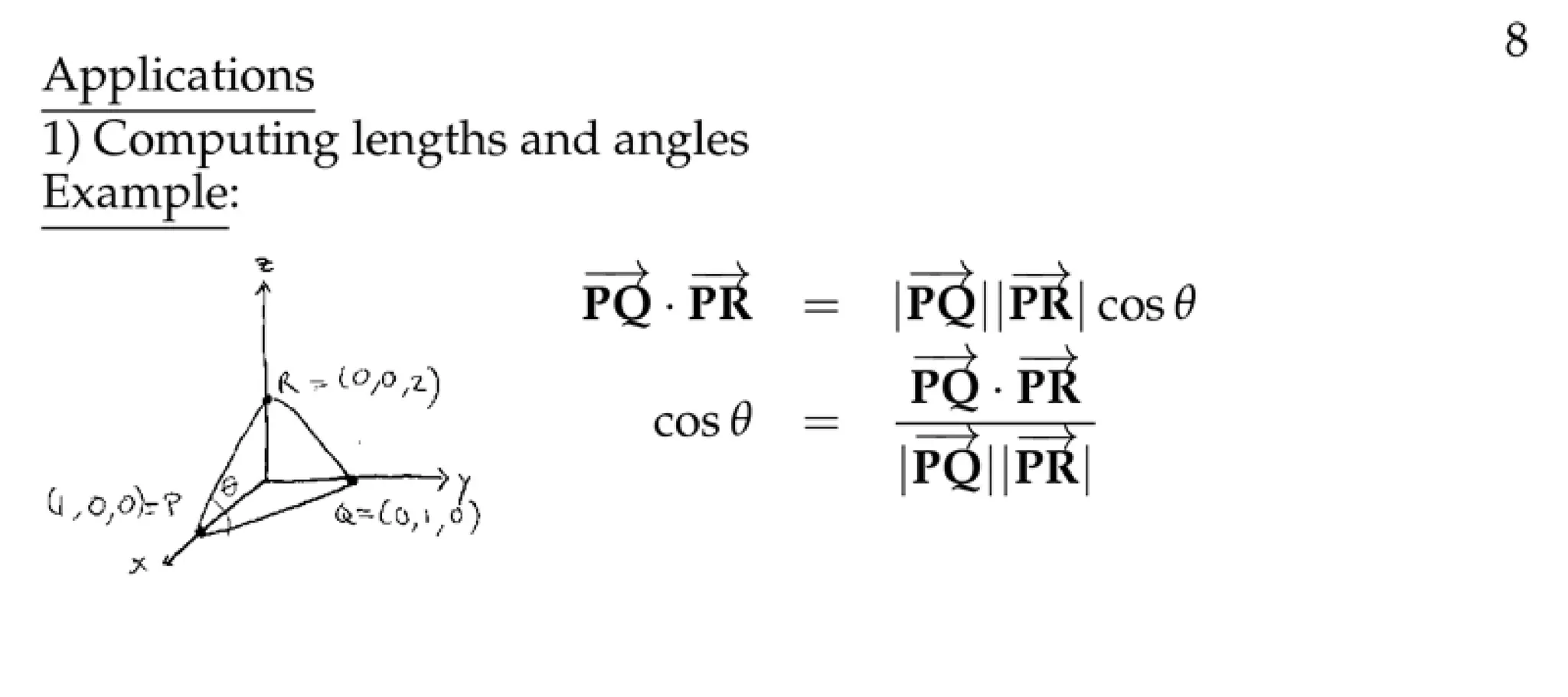
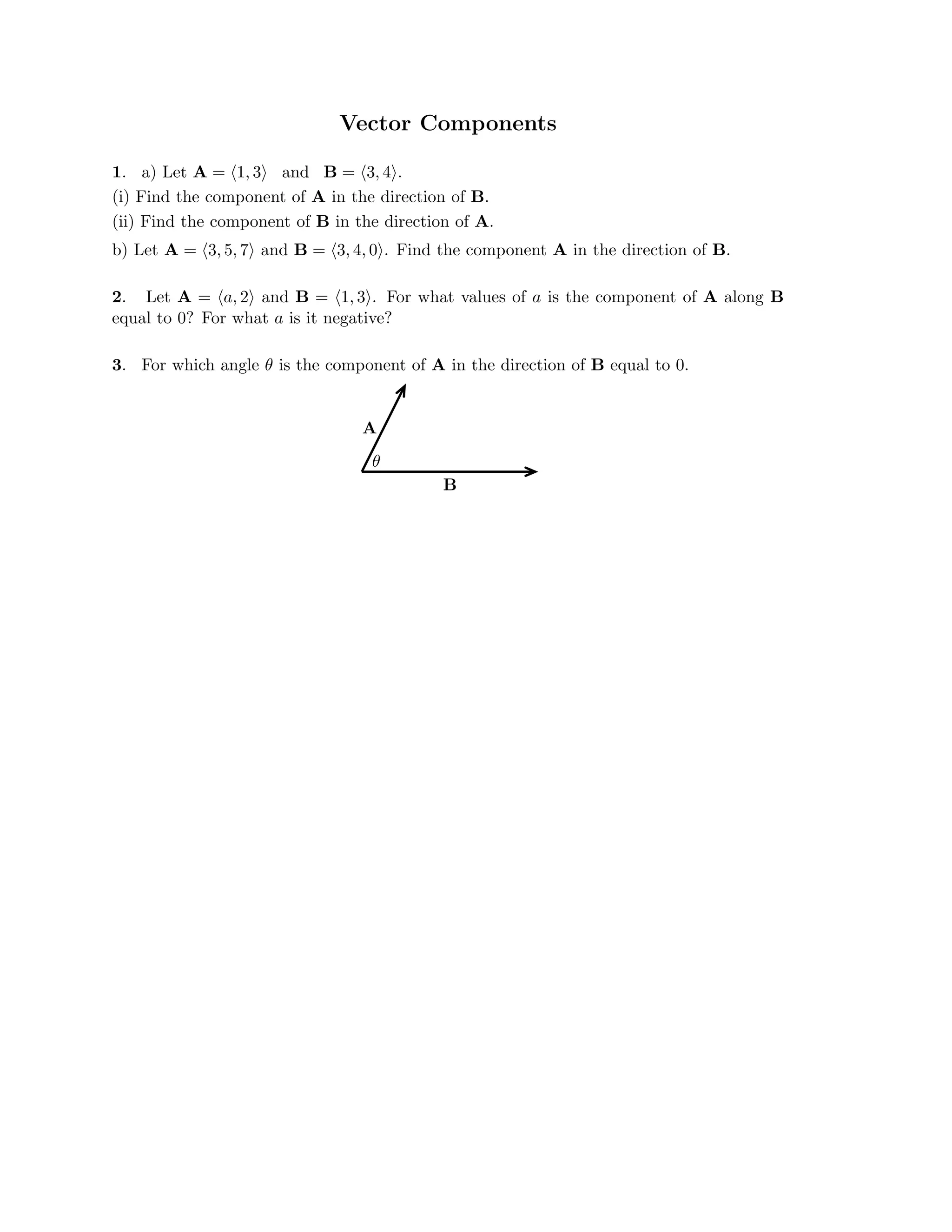
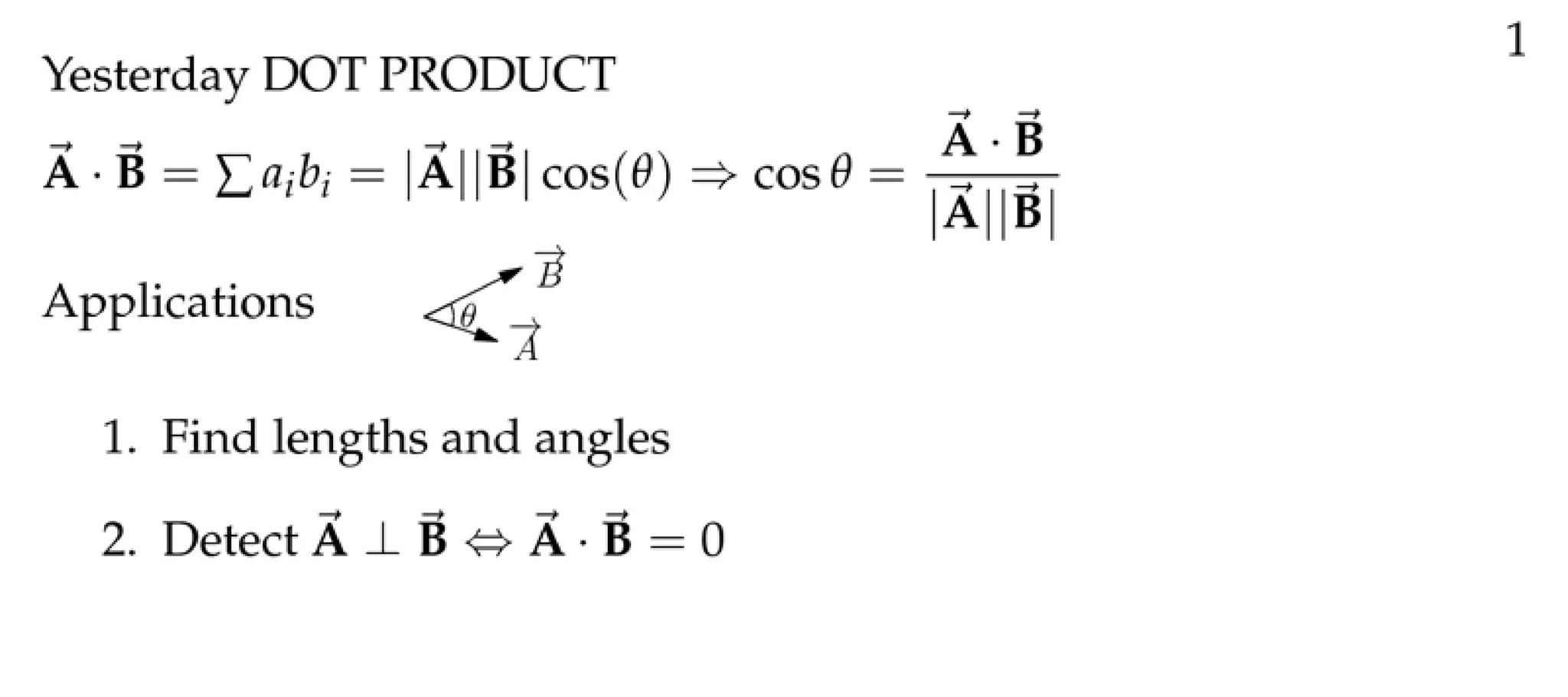
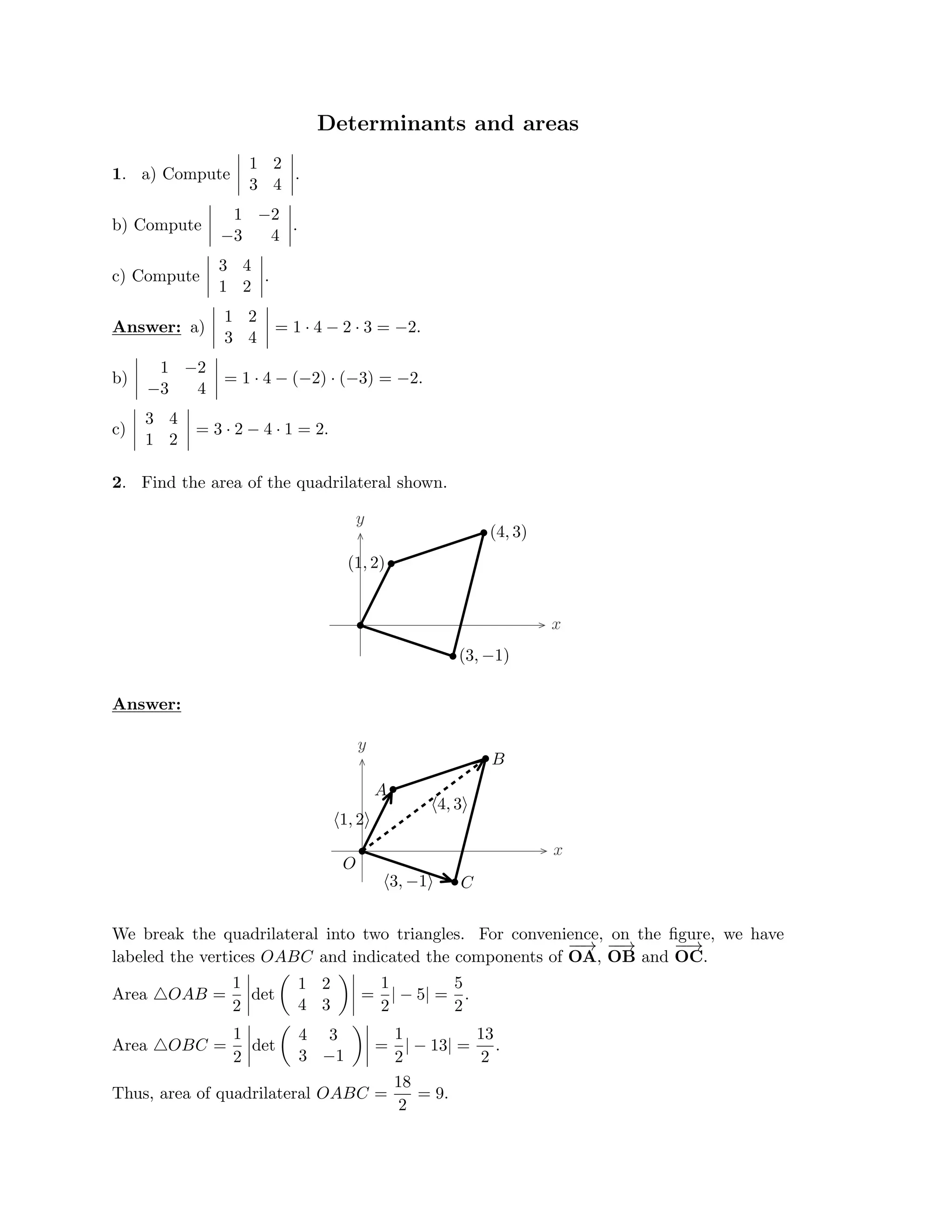
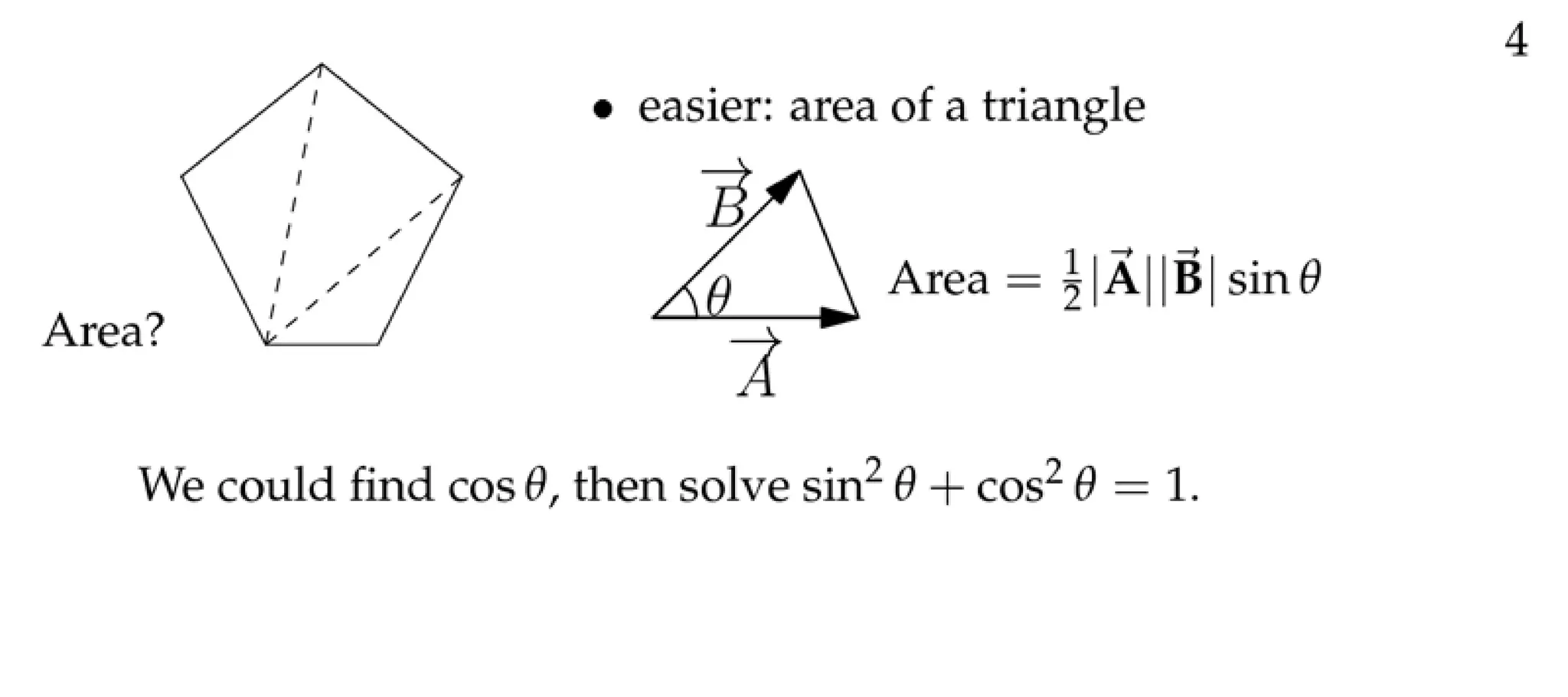
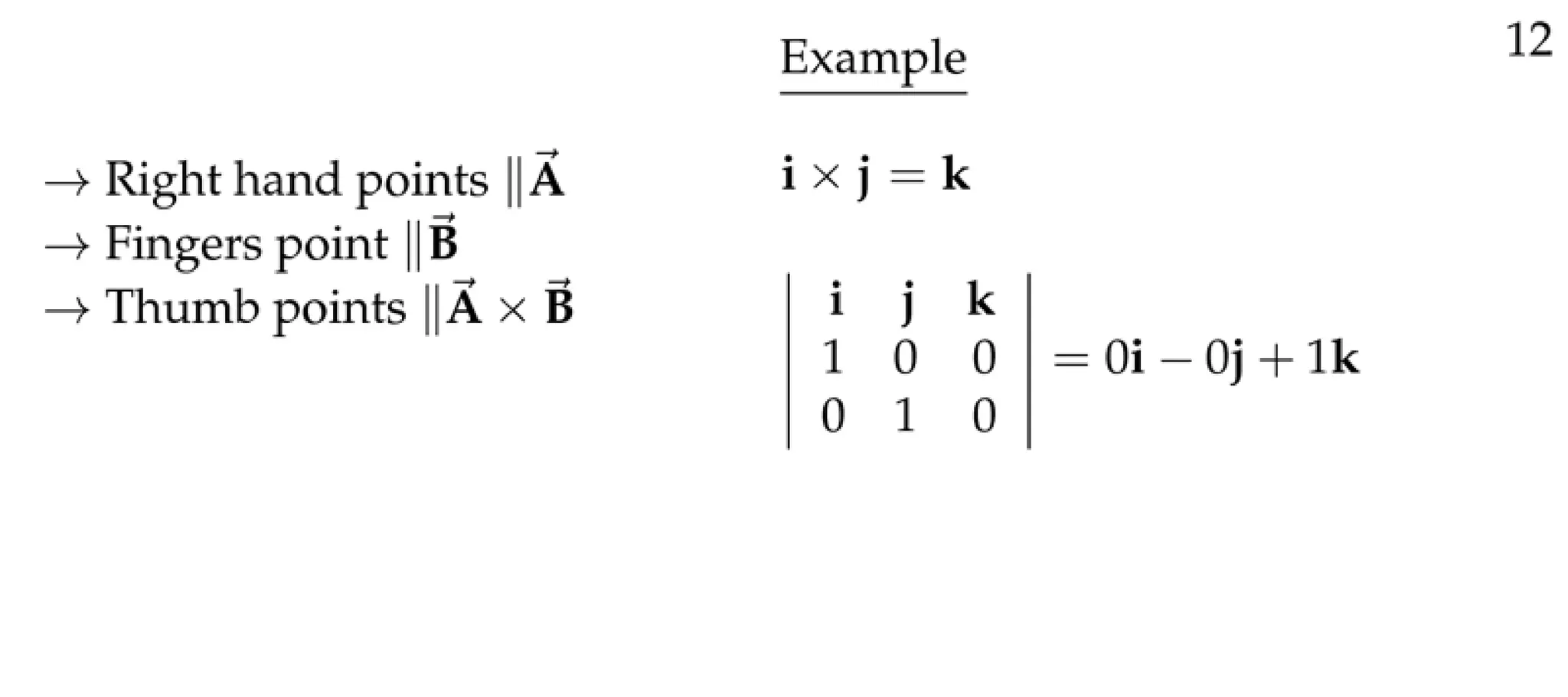
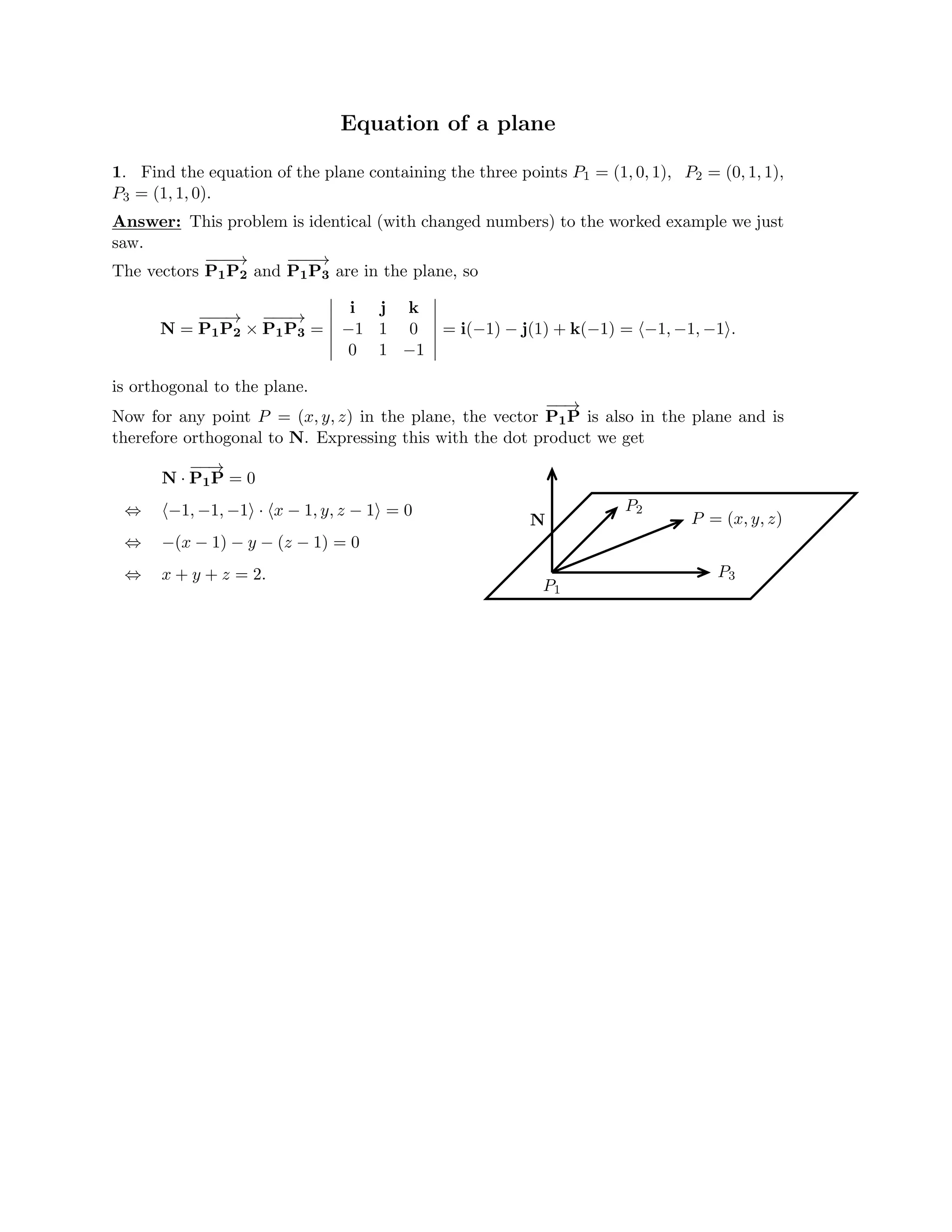
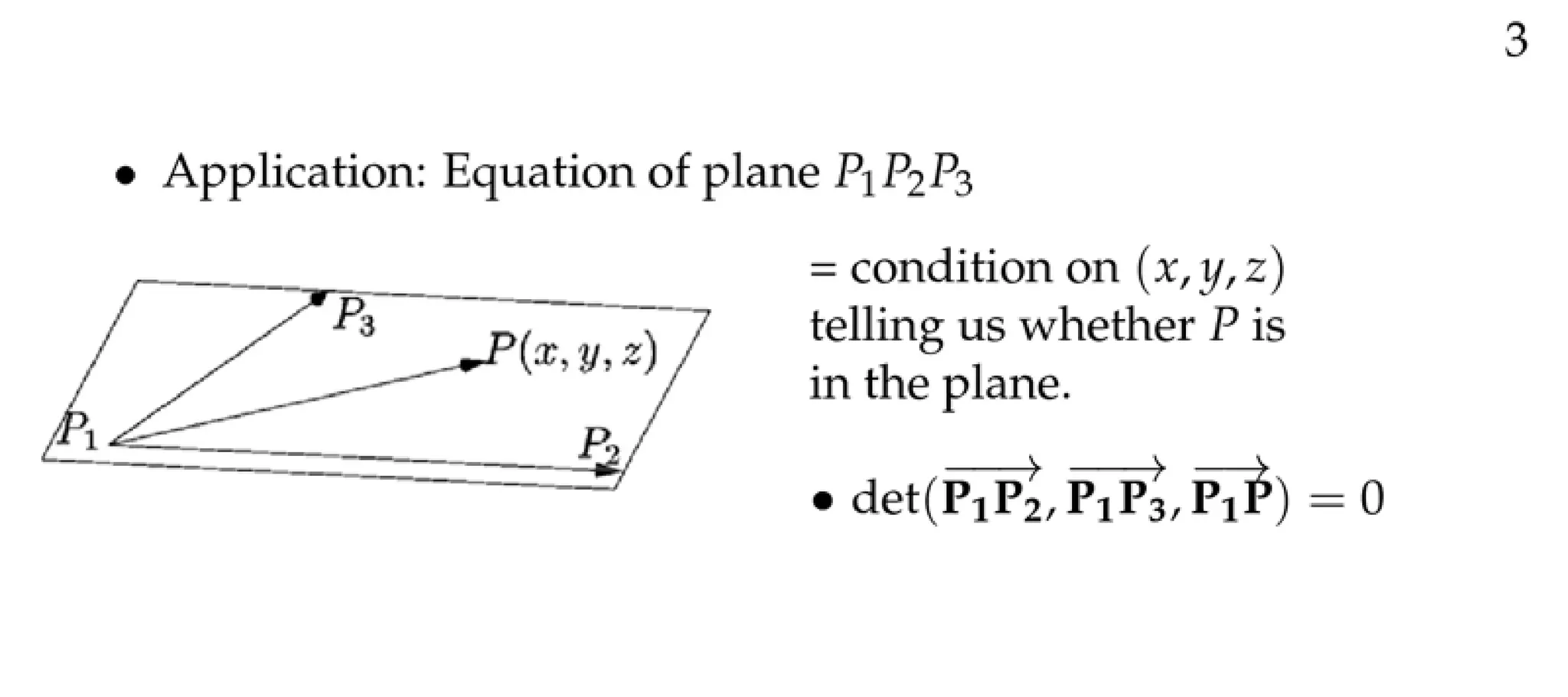
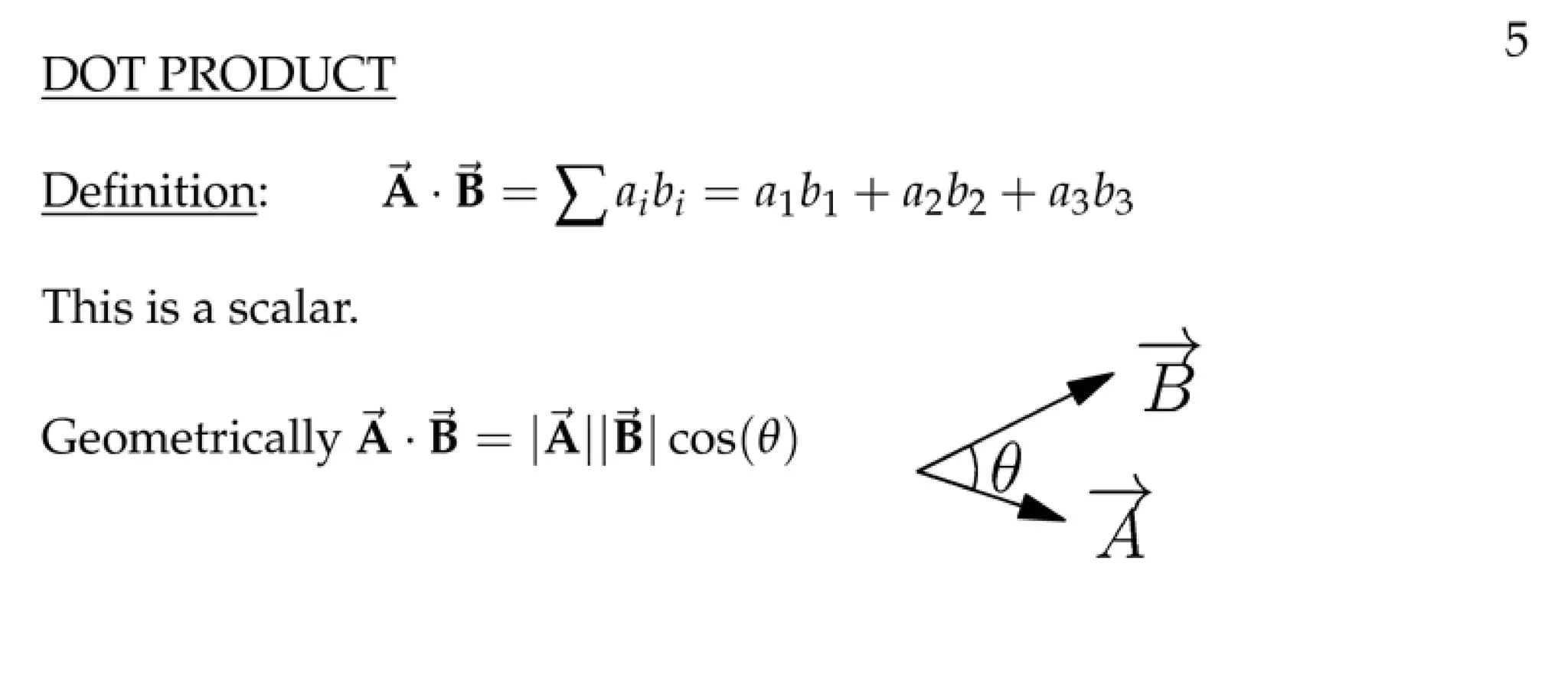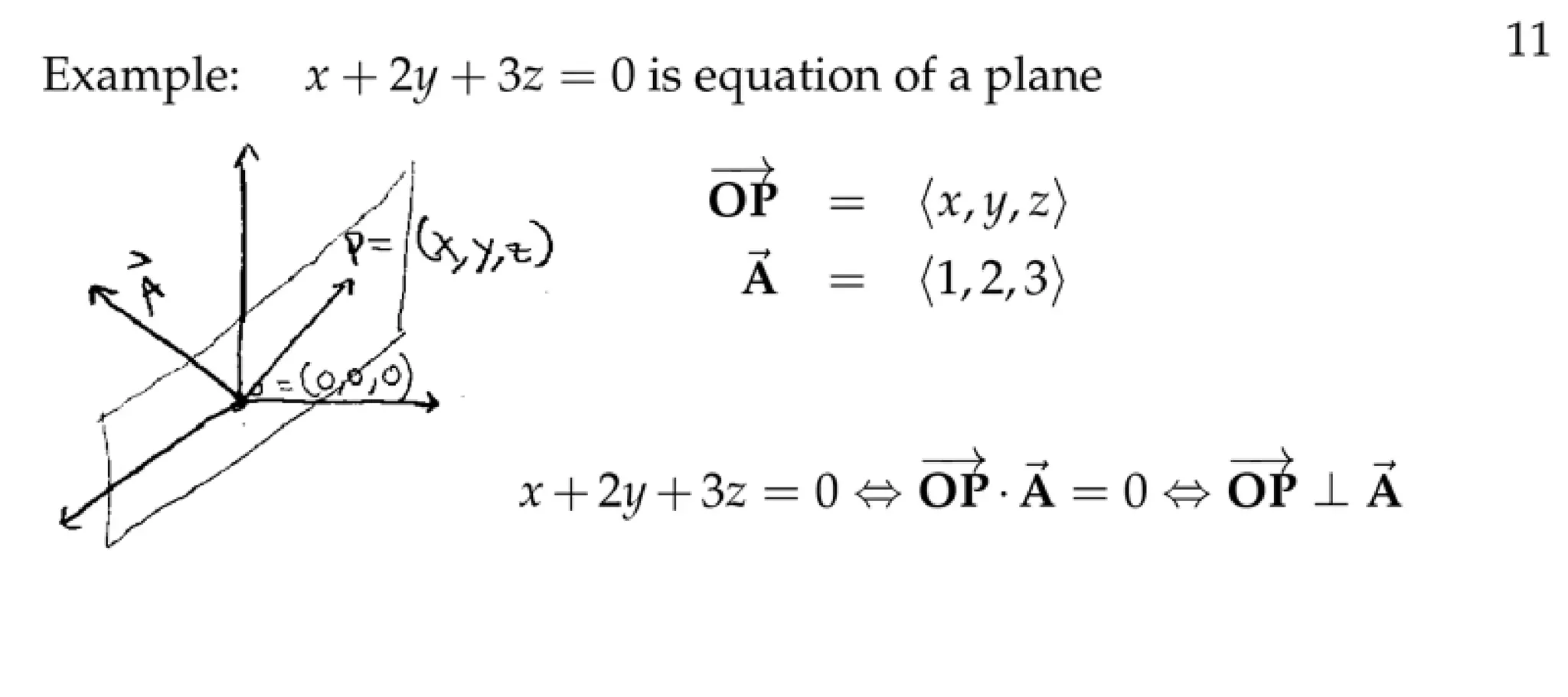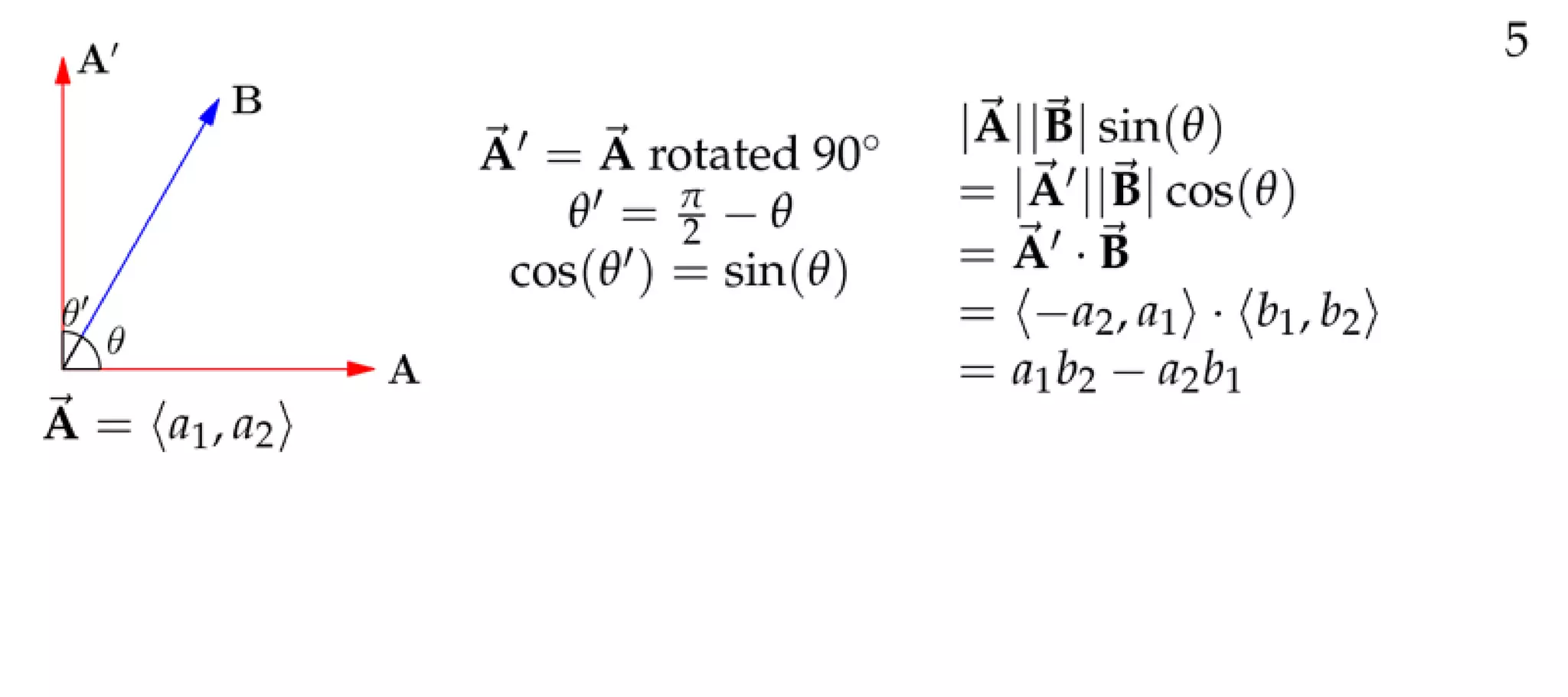The document defines a vector as having both magnitude and direction, represented geometrically by an arrow. It discusses representing vectors algebraically using coordinates, and defines operations like addition, subtraction, and scaling of vectors. Key vector concepts covered include the dot product, which yields a scalar when combining two vectors, and unit vectors, which have a magnitude of 1. Examples are provided of using vectors to solve problems and prove geometric properties.