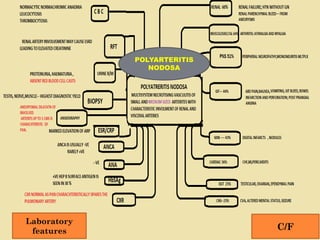
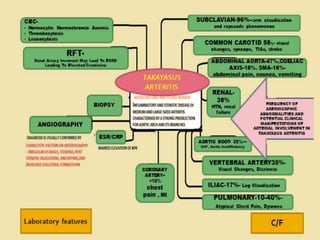
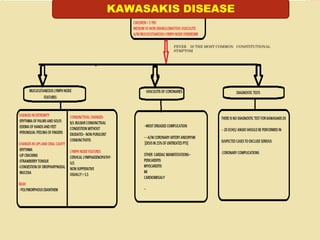
Vasculitis refers to inflammation of blood vessels. This document discusses vasculitis syndromes including definitions, classifications, clinical presentations, diagnostic evaluations, and management. Vasculitides are classified based on the size of vessels predominantly involved as large, medium, or small vessel. Common small vessel vasculitis includes Wegener's granulomatosis and microscopic polyangiitis. Treatment involves immunosuppressants such as cyclophosphamide, steroids, methotrexate, and biologics depending on severity and type of vasculitis. Prompt diagnosis and treatment is important to prevent organ damage from ischemia.