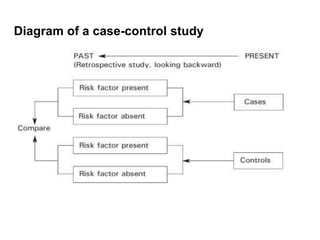
This document discusses variables, hypotheses, study types, and validity/reliability in research. It defines variables as characteristics that can take different values, and categorizes them as numerical, categorical, continuous, discrete, ordinal, and nominal. Hypotheses predict relationships between factors and problems that can be tested. Study types include descriptive studies, comparative/analytical studies, experimental studies, quasi-experimental studies, and before-after studies. Validity means measurements actually assess what is intended, while reliability means repeatability of findings.