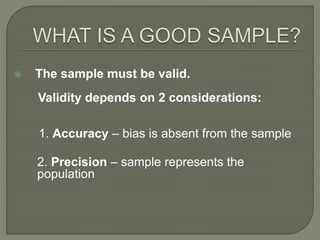
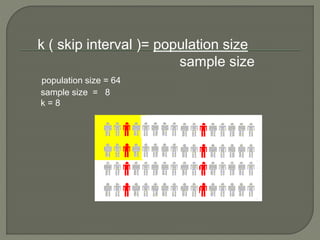
This document discusses sampling and sample size in statistics. It defines key terms like population, sample, sampling unit, sampling frame, and sampling schemes. It explains that sampling allows researchers to generalize results from a subset of the population. The main advantages of sampling are that it is less costly, takes less time, and can provide more accurate results than studying the entire population. The document also discusses different sampling methods like simple random sampling, systematic random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling. It notes that sample size depends on several factors and must result in a truly representative sample with small errors.