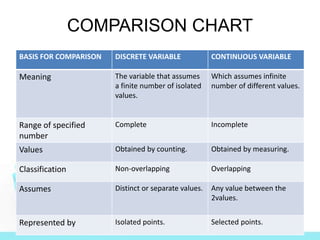
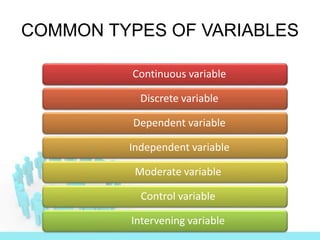
This document discusses different types of variables that can be studied in research. It defines a variable as a measurable characteristic that can change or vary. Variables are categorized as either continuous or discrete. Discrete variables can only take on distinct, countable values and include nominal and ordinal variables. Continuous variables can assume any value within a given range and include interval and ratio variables. Examples of each type of variable are provided.