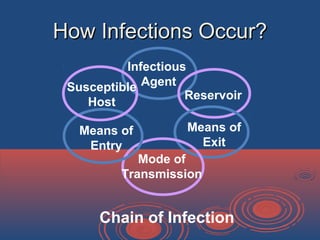
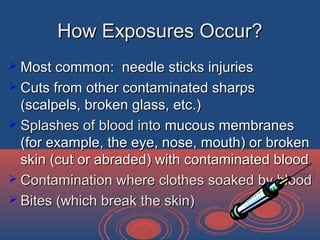
Standard precautions are control guidelines designed to protect healthcare workers from exposure to diseases spread by blood and other bodily fluids. They involve assuming that all human blood and bodily fluids are potentially infectious. Key elements of standard precautions include hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment like gloves and gowns, safe disposal of sharps, and cleaning and disinfection of surfaces contaminated with blood or bodily fluids. Standard precautions aim to prevent transmission of pathogens through contact with blood or bodily fluids and should be applied universally to all patients.