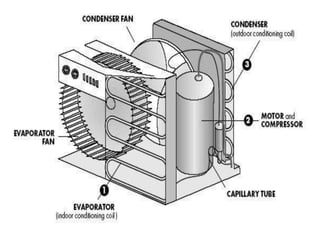
The document serves as an introductory lecture on Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration (HVAC) engineering, covering essential topics such as the basics of HVAC, the vapor compression cycle, and performance metrics like the energy efficiency ratio. It explains the processes involved in heating, cooling, ventilation, and refrigeration systems, along with relevant diagrams for understanding the vapor compression refrigeration system. The document outlines the key performance indicators and different cases for the vapor compression cycle, emphasizing the importance of efficiency in HVAC systems.