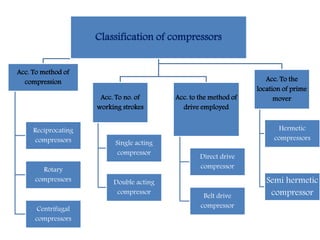
This document discusses refrigerant compressors, including their classification and types. It describes reciprocating compressors, which use pistons driven by a crankshaft to compress gases. Rotary compressors are also covered, using two meshing screws to compress gas. Centrifugal compressors rely on the kinetic energy of an impeller to increase pressure. Direct drive and belt drive compressors are compared, as well as hermetic and semi-hermetic compressors, which enclose components within a sealed shell.