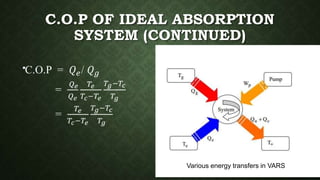
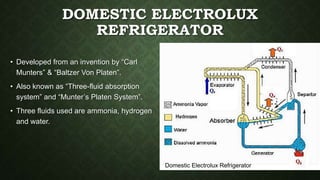
The document discusses vapour absorption refrigeration systems. It describes a simple vapour absorption system using ammonia and water, and a practical system. It defines the coefficient of performance (COP) of an ideal absorption system and lists properties desired in ideal refrigerants and absorbents. The document also discusses the domestic Electrolux refrigerator, which uses ammonia, hydrogen and water, and operates entirely through gravity flow without pumps. Key advantages of absorption systems over compression include having no moving parts and ability to operate on thermal energy alone.