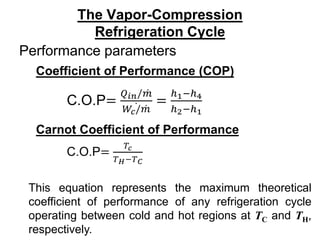
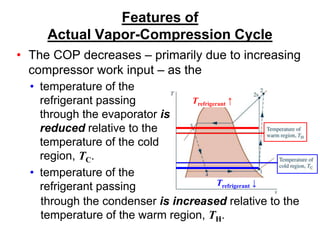
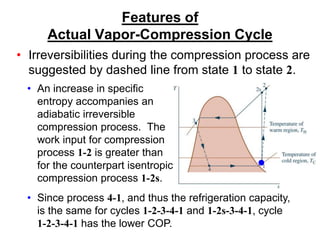
The document summarizes the vapor compression refrigeration cycle. It consists of four main processes: (1) evaporation in the evaporator, (2) compression in the compressor, (3) condensation in the condenser, and (4) expansion in the expansion valve. Heat is transferred from the refrigerated space during evaporation and to the surroundings during condensation. The coefficient of performance (COP) measures the efficiency of the cycle and is lower for actual cycles compared to the theoretical Carnot COP due to irreversibilities. Refrigerant selection considers performance, safety, environmental impact, and global warming potential.