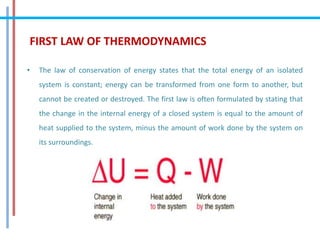
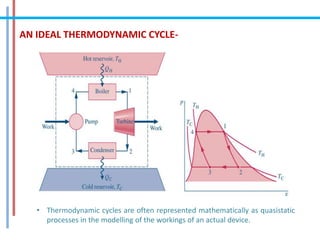
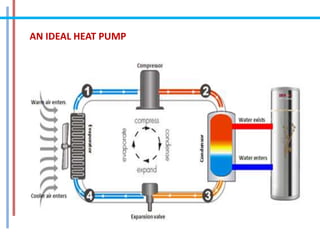
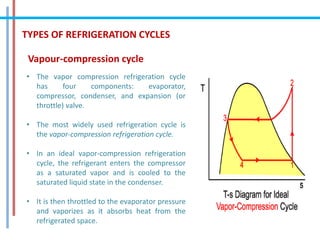
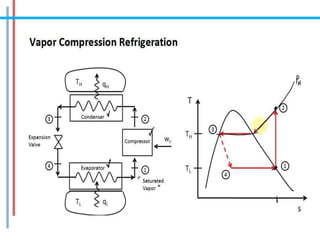
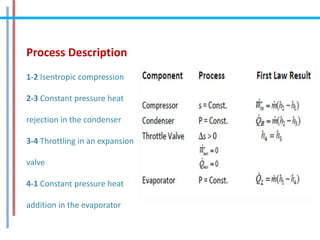
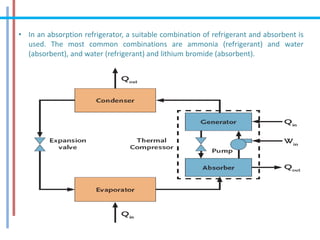
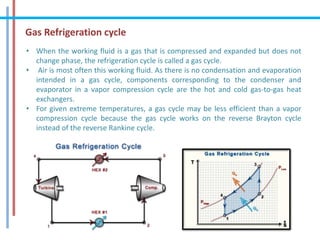
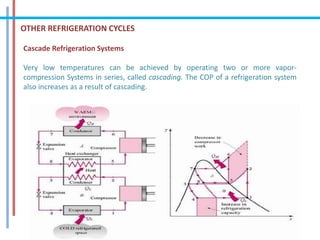
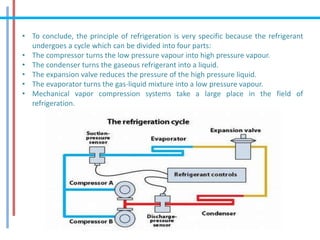
The document provides a comprehensive overview of refrigeration cycles and thermodynamic principles, primarily focusing on the first law of thermodynamics and various types of refrigeration cycles, including vapour compression and absorption cycles. It explains how thermodynamic cycles function as either heat engines or heat pumps and details the components and processes involved in these cycles. Additionally, it highlights alternative refrigeration systems, such as gas refrigeration cycles and thermoelectric refrigeration, illustrating their applications and efficiencies.