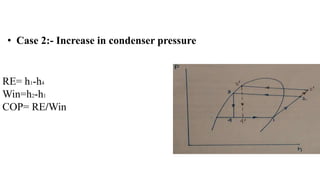
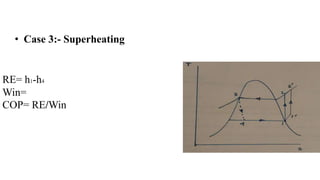
Vapour compression refrigeration cycle uses four main components - a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. The refrigerant is compressed into a hot, high-pressure gas (1-2), condensed into a liquid in the condenser (2-3), expanded through the throttle valve into a cold, low-pressure liquid-vapour mixture (3-4), and evaporated in the evaporator (4-1) to complete the cycle. The coefficient of performance (COP), a measure of efficiency, is calculated as the refrigeration effect divided by the work input. Increasing the evaporator or condenser pressure decreases COP, while superheating may increase or decrease COP depending on the refrigerant