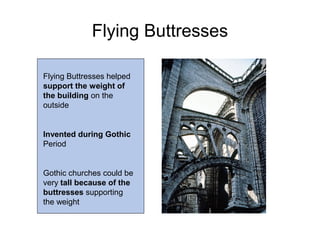
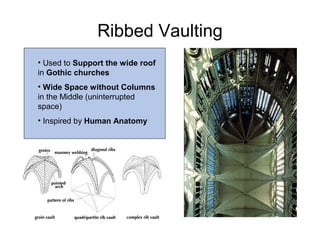
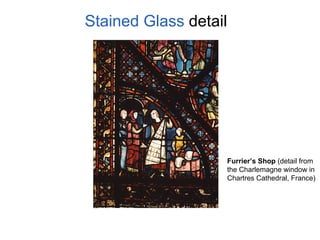
Gothic art and architecture emerged in Europe between the 12th and 15th centuries, expressing Christian political and religious values. Key characteristics included tall buildings supported by flying buttresses and rib vaulting, vast stained glass windows illuminating interiors, and sculptures like the Virgin and Child. Major Gothic cathedrals included Saint-Denis, Notre Dame de Paris with its rose window, and Sainte-Chapelle known for its stained glass. Artists like Giotto began using techniques like linear perspective and realistic proportions.