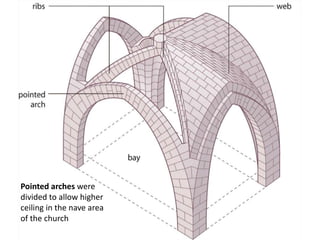
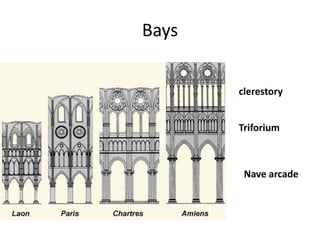
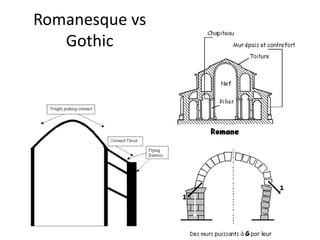
The document discusses Gothic art and architecture from the 12th to 16th centuries in France and England. It begins by introducing Gothic style, noting its emergence in France under Abbot Suger at Saint-Denis. Suger introduced innovations like rib vaults, pointed arches, rose windows, and stained glass, creating a new sense of light, space, and verticality. The document then examines key Gothic cathedrals like Chartres and Amiens that featured soaring vaults and vast stained glass areas. It traces the evolution of Gothic sculpture and the spread of Gothic styles across Europe.