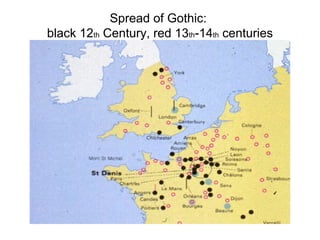
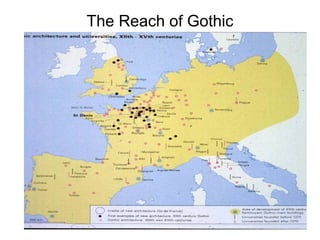
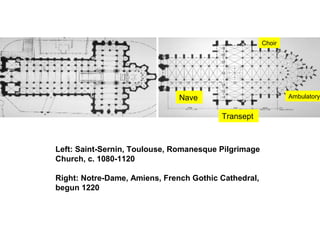
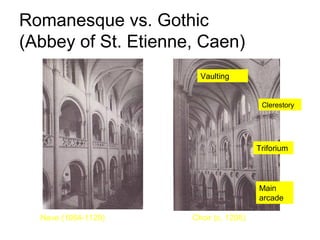
The document discusses the rise and spread of Gothic architecture between the 12th and 15th centuries. It began in France at St. Denis and was characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, flying buttresses, and larger windows to admit more light. Gothic cathedrals grew dramatically in scale and were a symbol of civic pride and rivalry between towns. Styles evolved from early Gothic to Rayonnant/High Gothic and Flamboyant Gothic. Gothic sculpture and painting also became more realistic and expressive during this period.