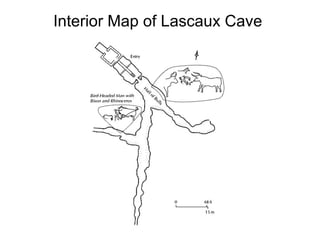
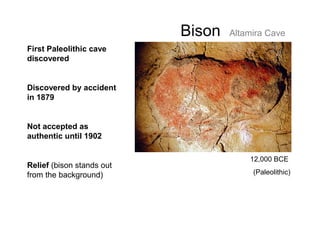
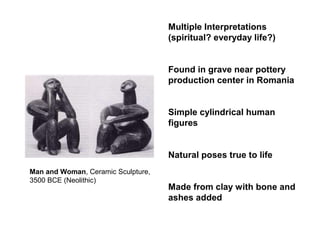
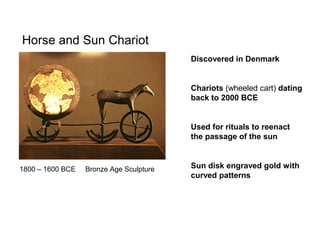
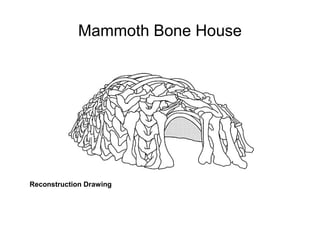
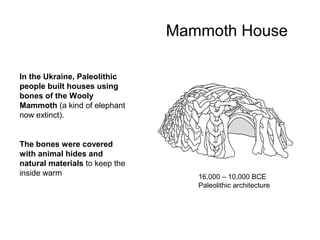
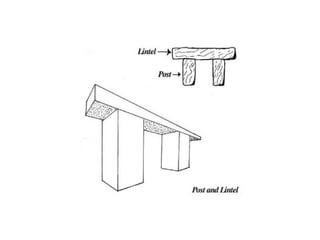
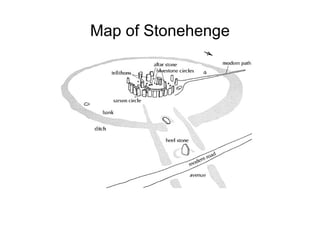
This document provides an overview of prehistoric art before written history. It describes how early humans first emerged in Africa and then spread across the globe. The prehistoric period is broken down into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic ages defined by the materials used like stone, bronze, and iron. Some of the most famous prehistoric cave paintings were found at sites like Lascaux, Altamira, and Chauvet Caves between 15,000-30,000 BCE. Sculptures and figurines from this era often depicted animals and fertility goddesses. Neolithic peoples began constructing permanent structures like mammoth bone houses and sites like Stonehenge that may have served ceremonial purposes.