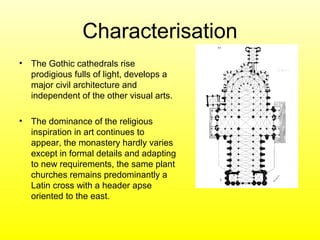
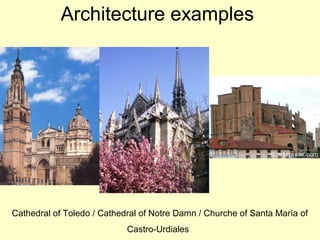
Gothic art developed in Western Europe from the Middle Ages through the Renaissance. Some key aspects include elaborate cathedrals built starting in northern France using flying buttresses and stained glass windows to let in maximum light. Gothic architecture was characterized by pointed arches and vaulted ceilings in cathedrals, while Gothic sculpture moved towards more naturalism and realistic figures. Gothic painting included frescoes, stained glass windows, illuminated manuscripts, and later oil paintings on canvas as artistic styles evolved over centuries.