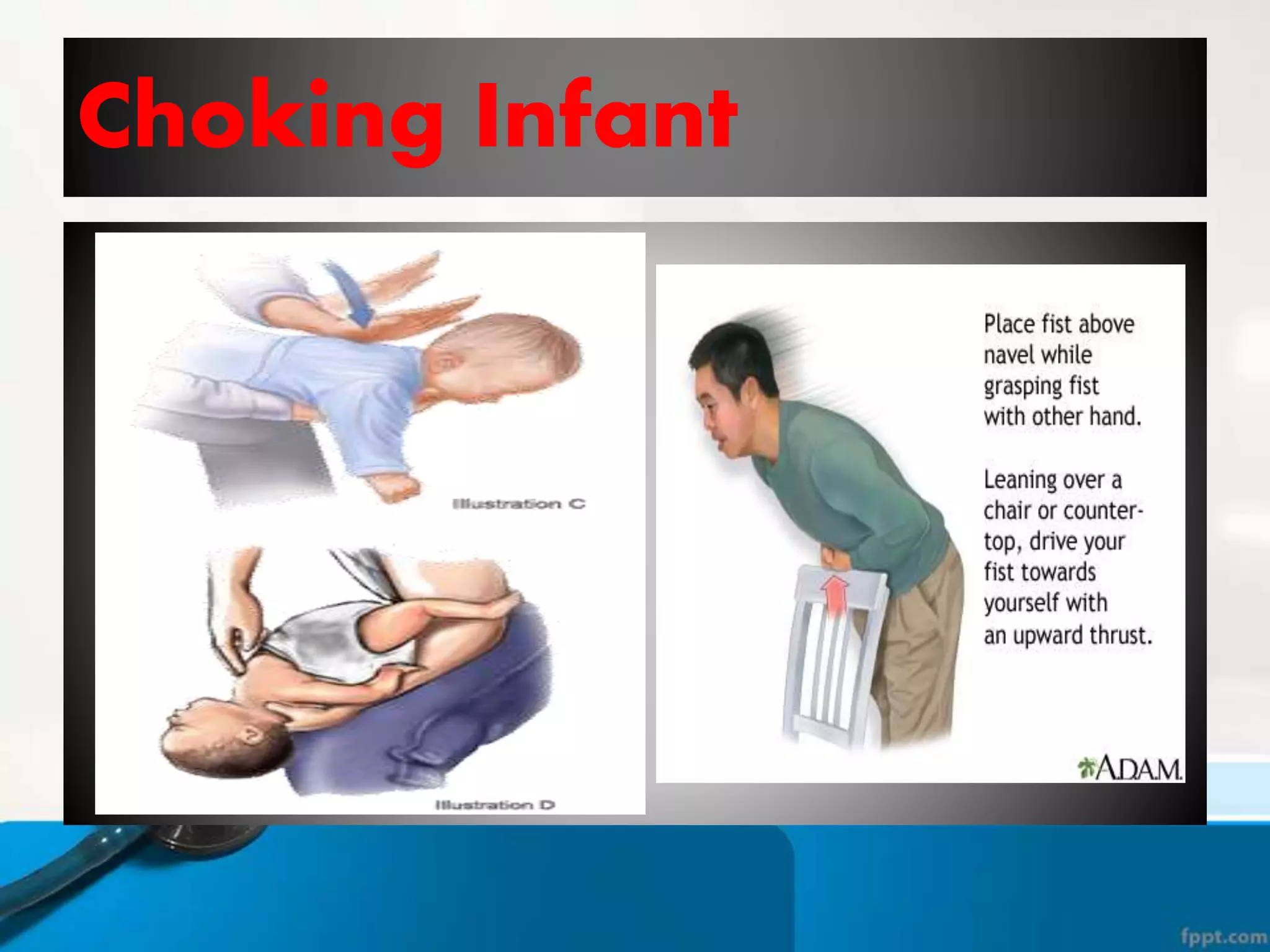
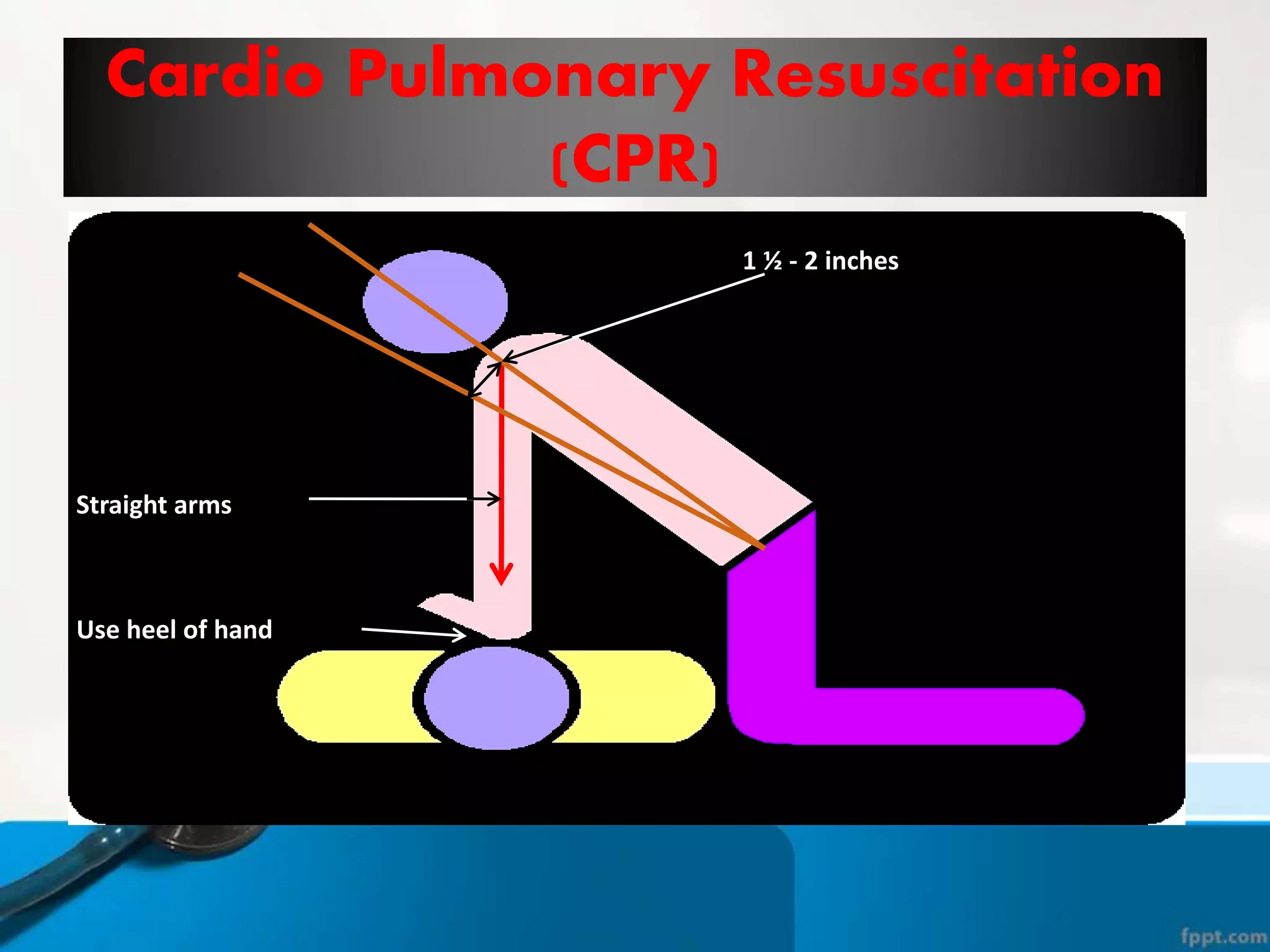
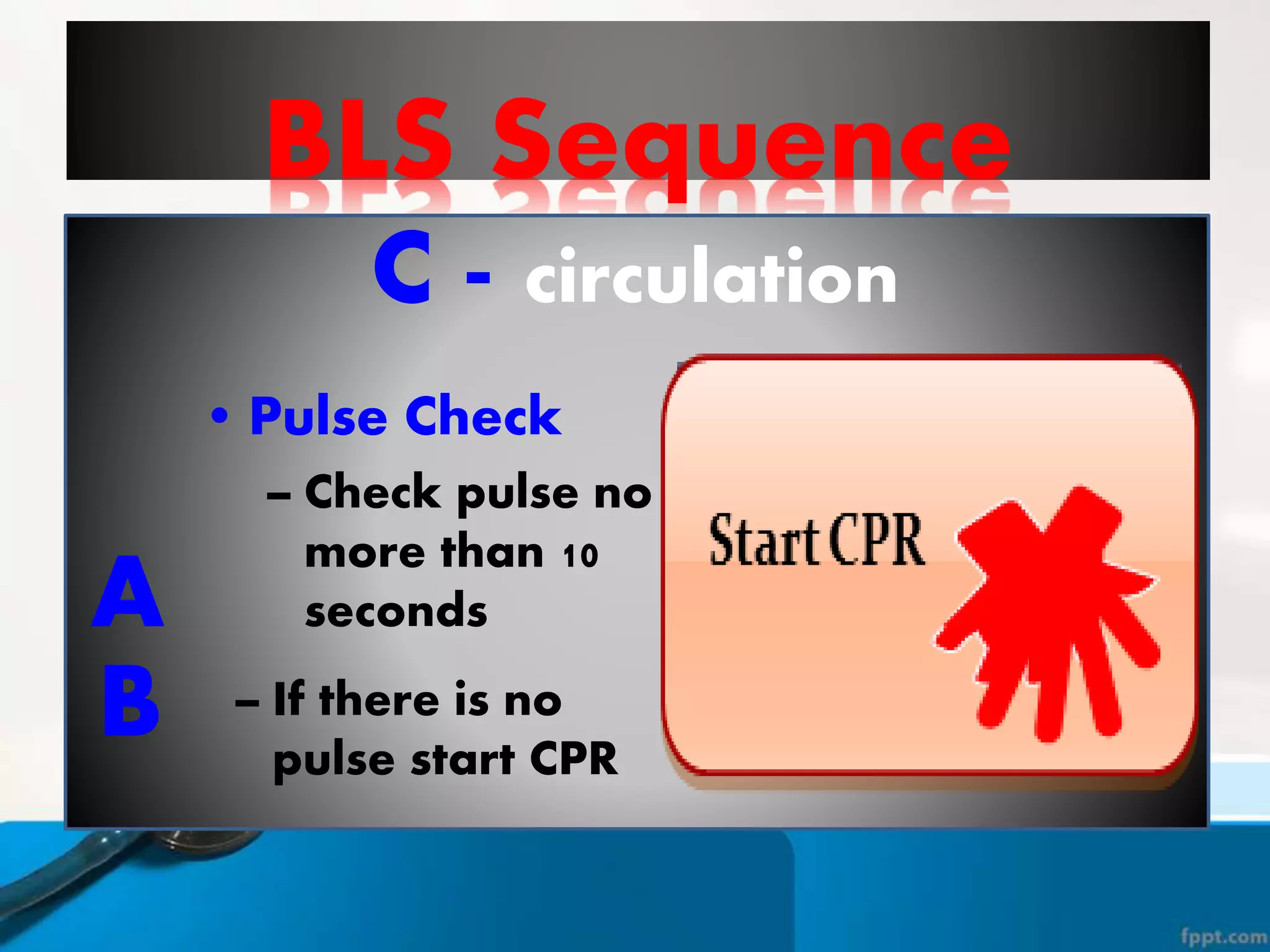
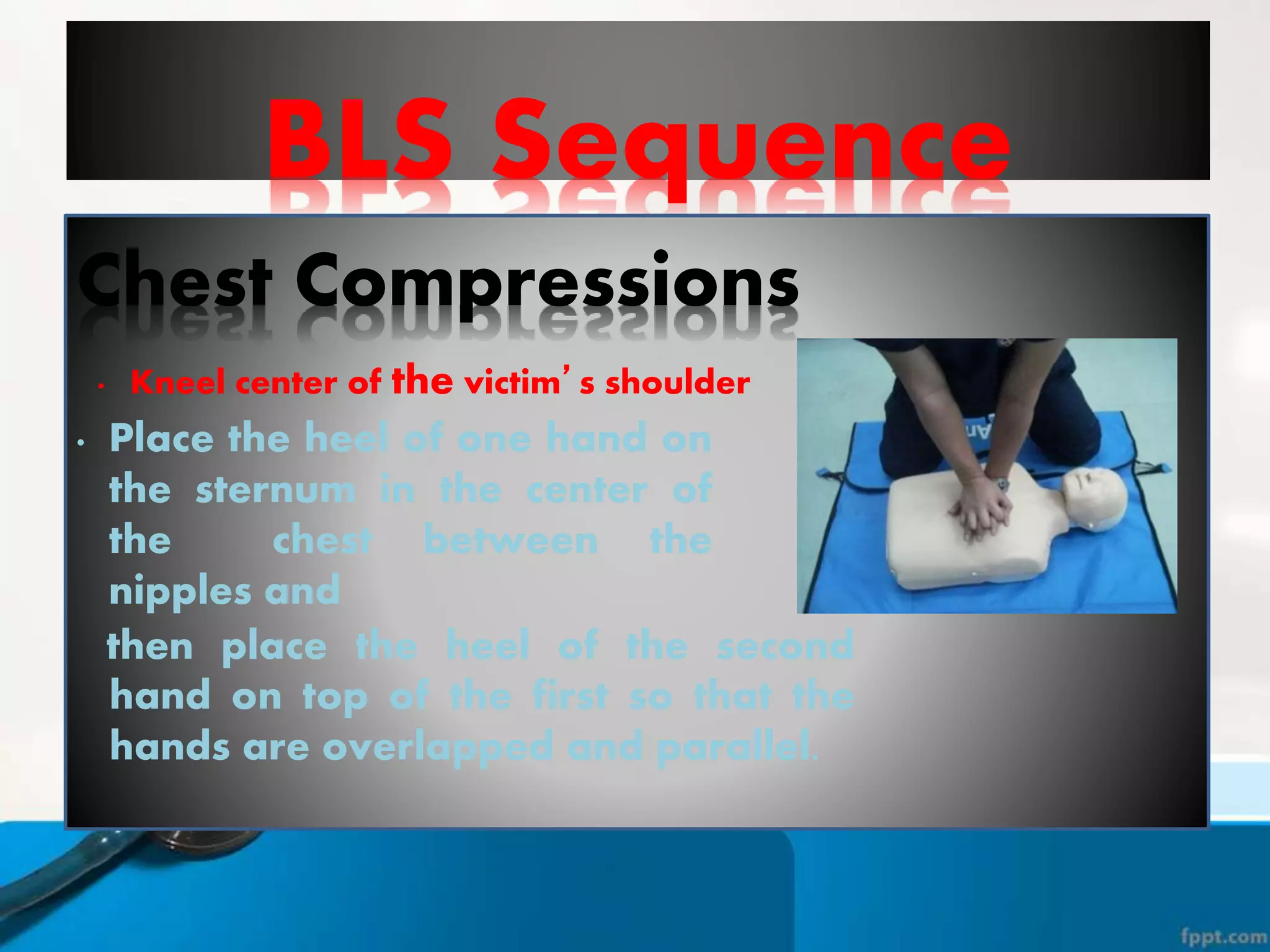
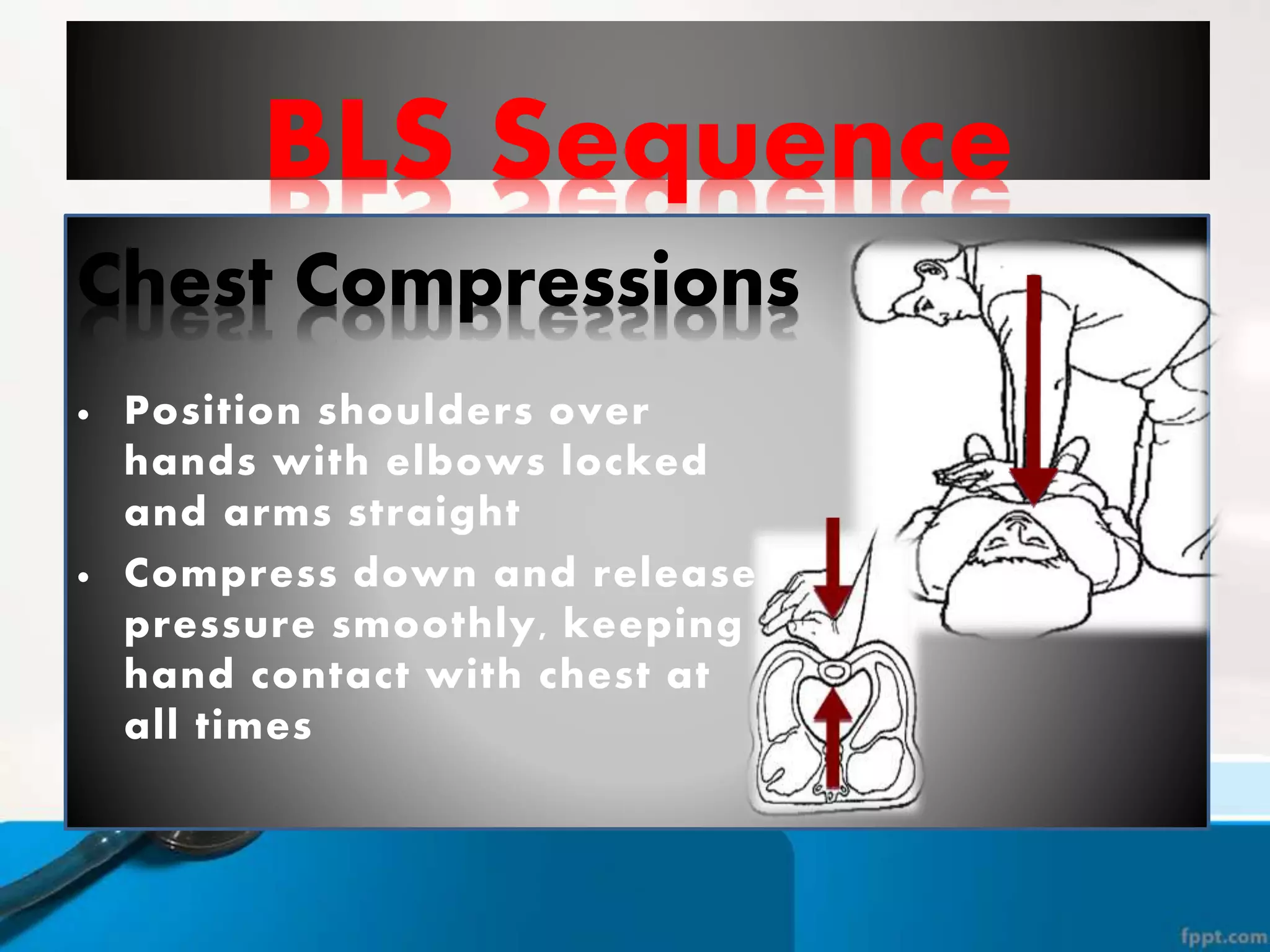
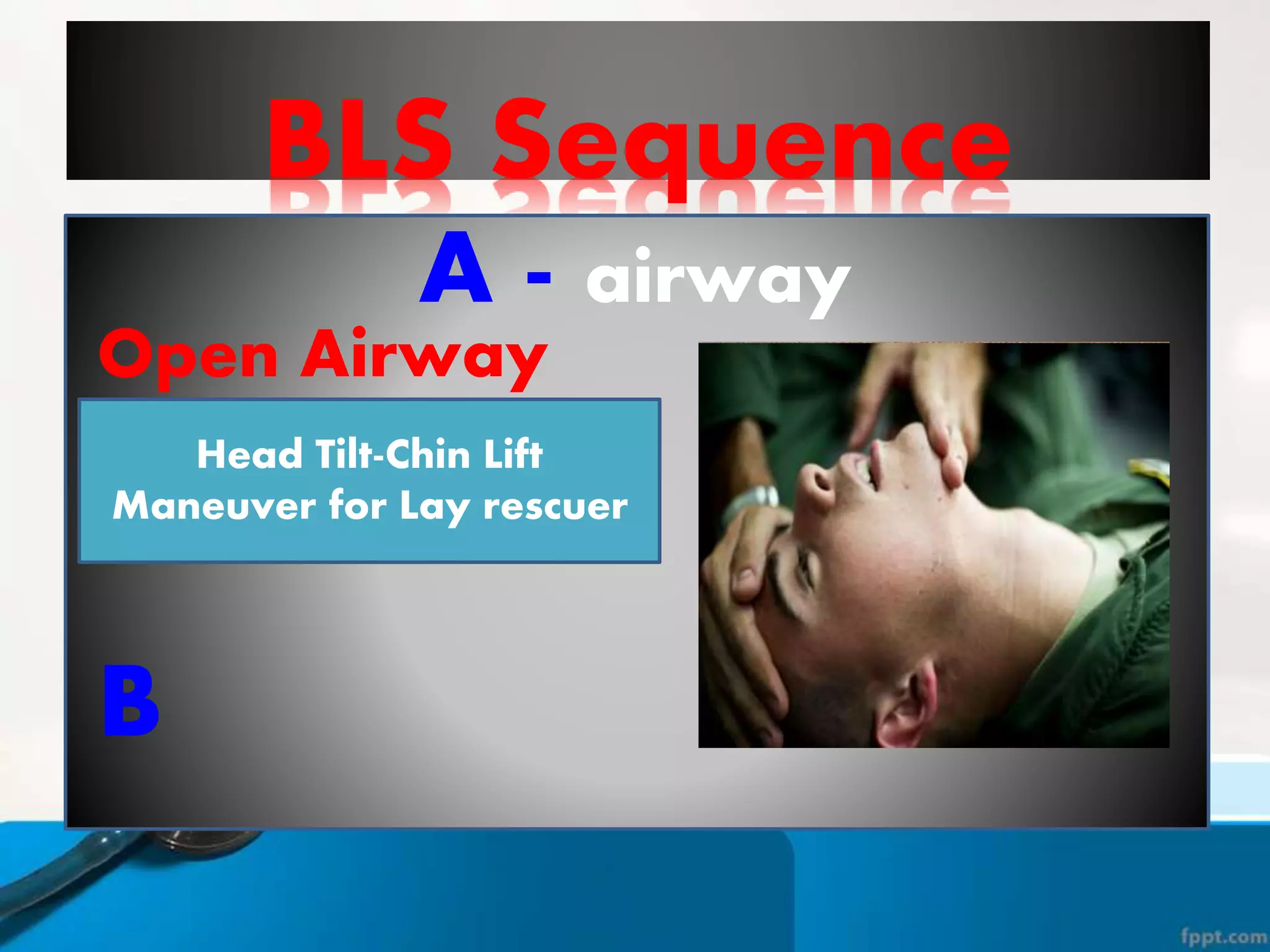
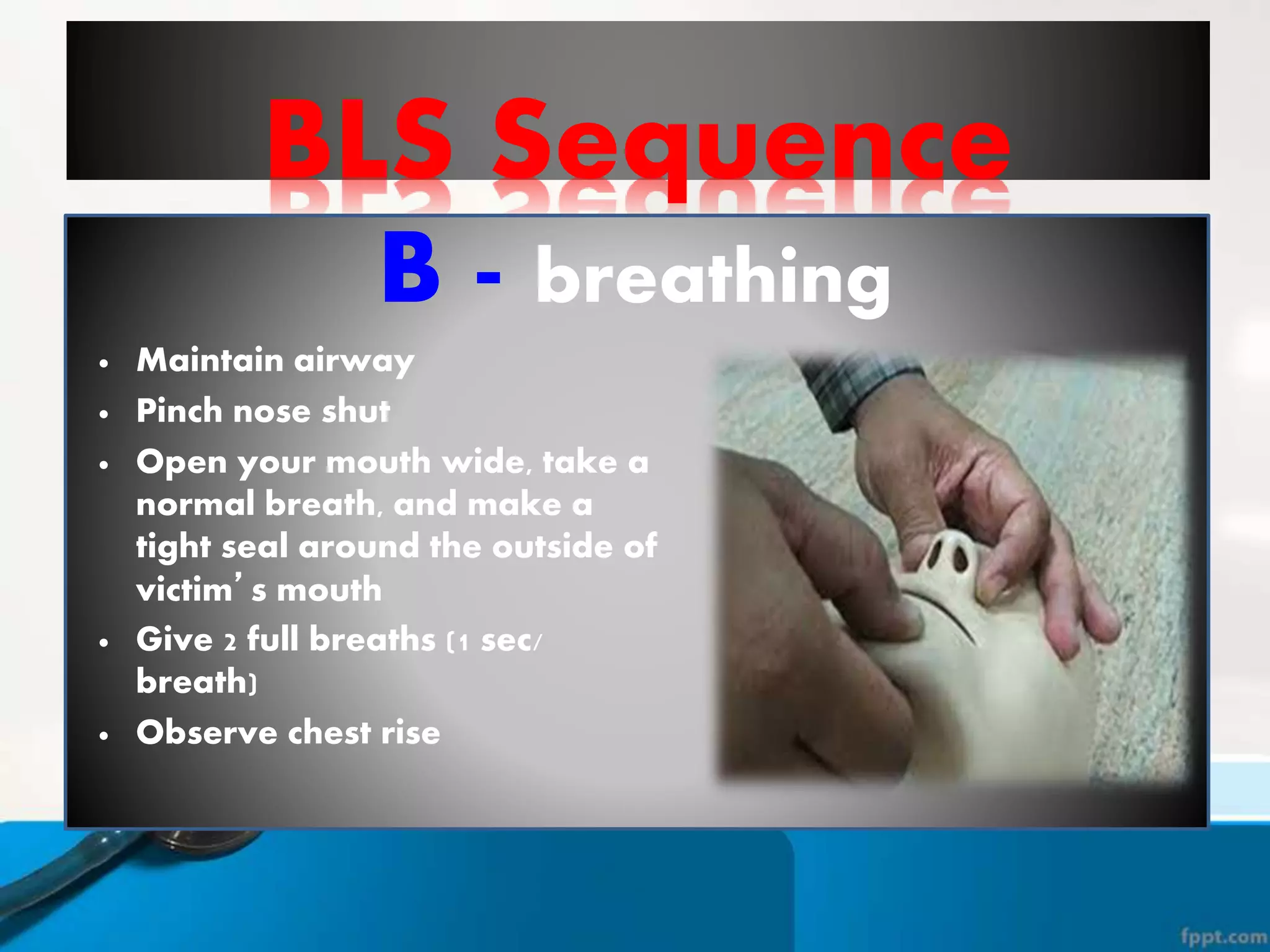
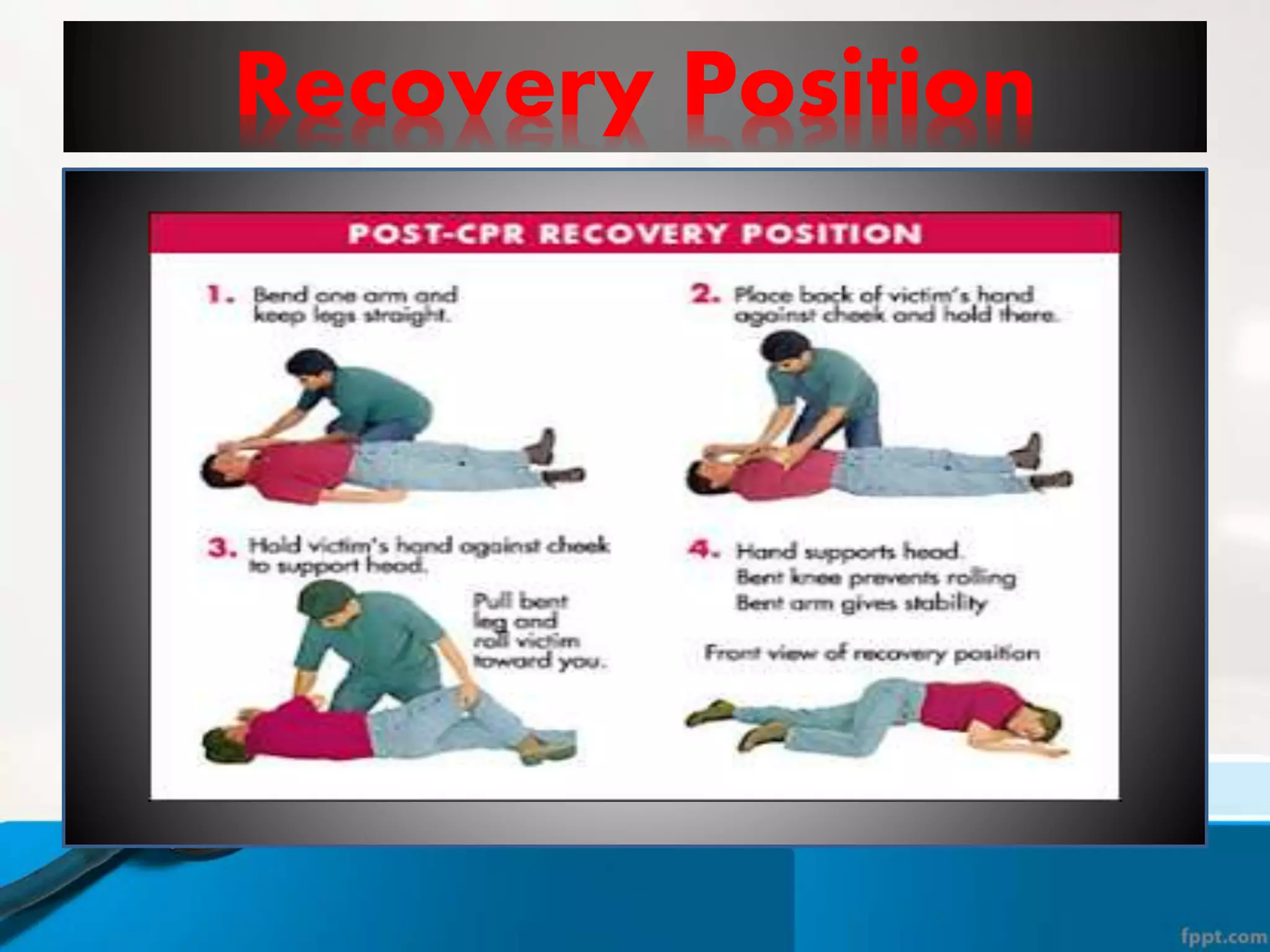
This document provides instructions for basic life support techniques including the Heimlich maneuver and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). It outlines 5 learning objectives and describes procedures for choking in adults, children, and infants as well as CPR techniques for adults, children, and infants. The BLS sequence of checking for danger, responsiveness, pulse, providing breaths, and chest compressions is explained. Indications for when to start and stop CPR are also reviewed.