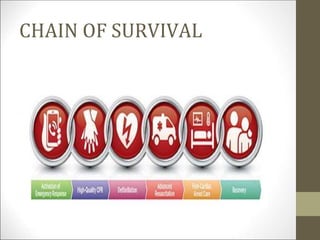
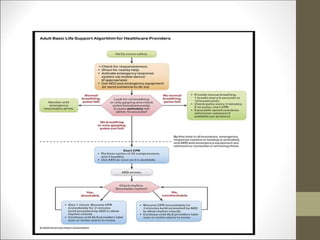
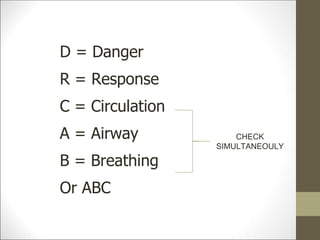
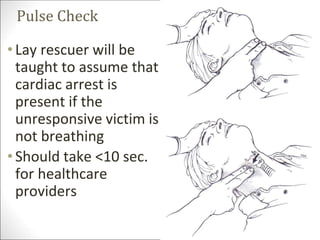
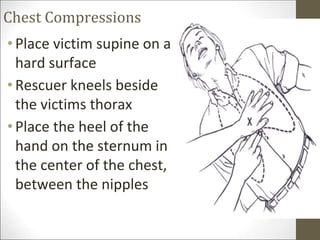
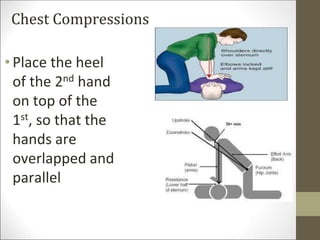
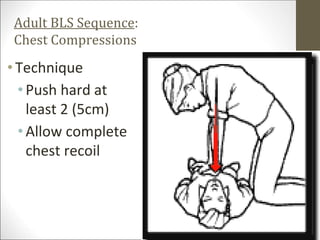
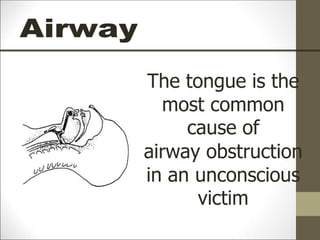
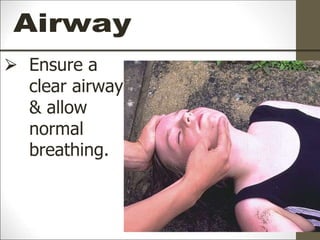
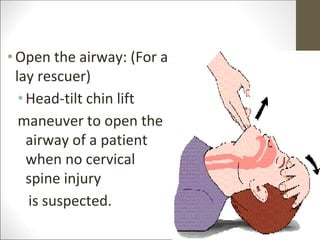
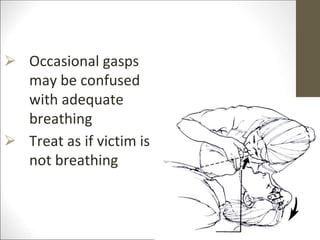
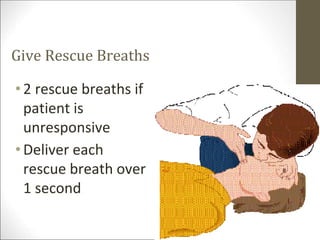
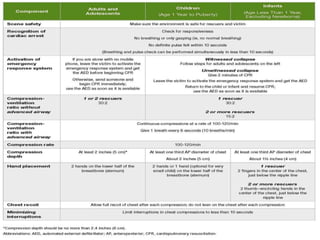
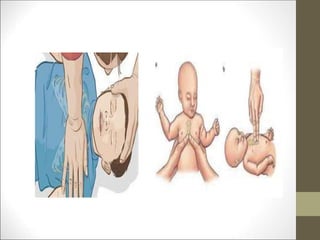
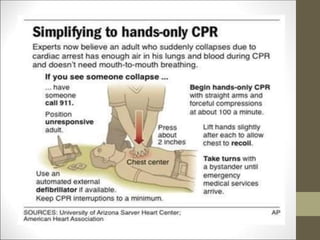
Basic life support (BLS) involves providing chest compressions and rescue breathing to victims of cardiac arrest. It is crucial for sustaining life until advanced medical care can be provided. The primary survey in initial assessment follows the DRABC (danger, response, circulation, airway, breathing) protocol to assess safety, level of consciousness, breathing, and pulse. For an unresponsive victim without breathing or pulse, the rescuer should immediately call for help, retrieve an AED, and begin high-quality chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute with full chest recoil and minimal interruptions, paired with rescue breaths at a 30:2 compression-to-ventilation ratio. CPR should continue until spontaneous