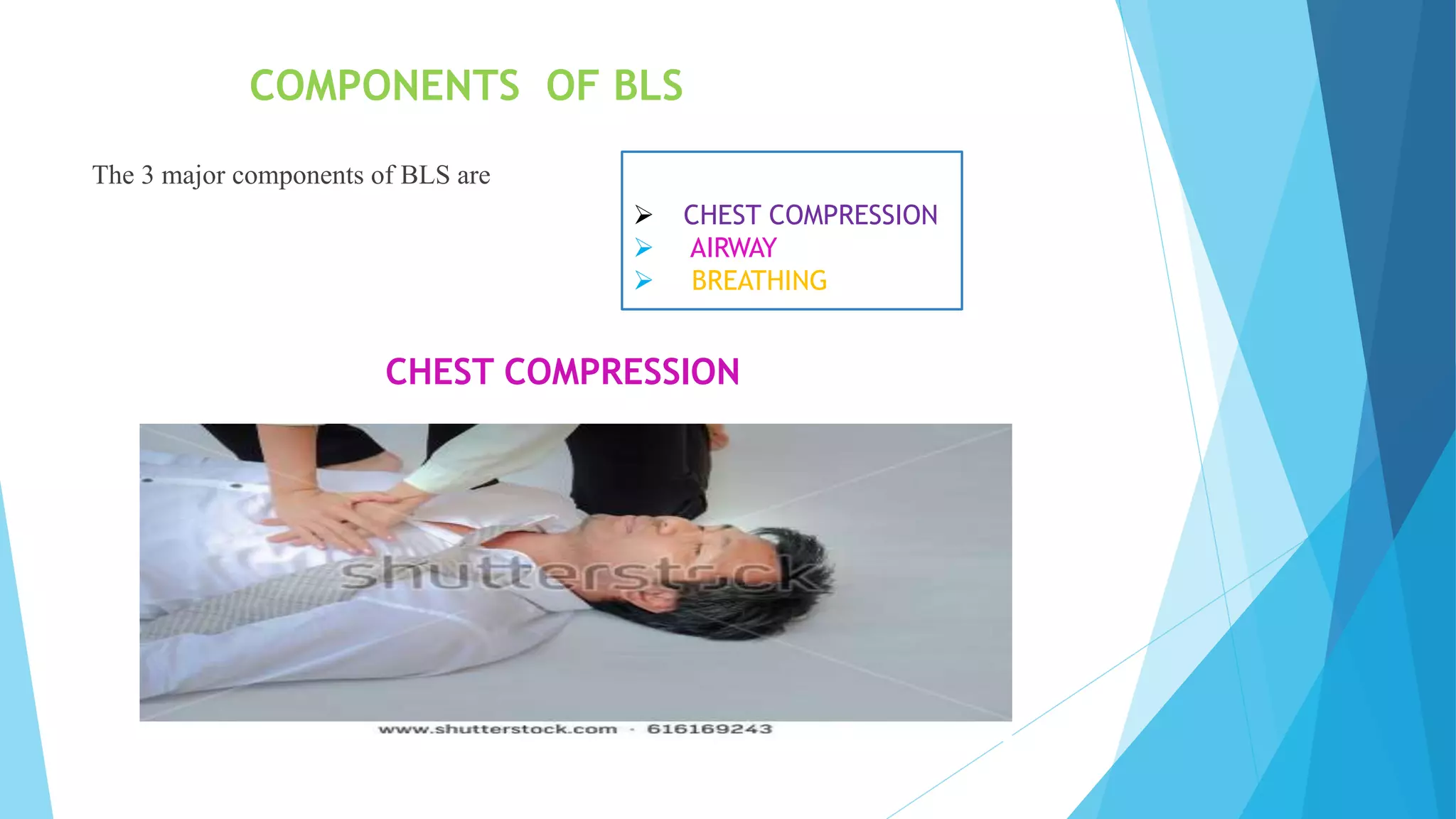
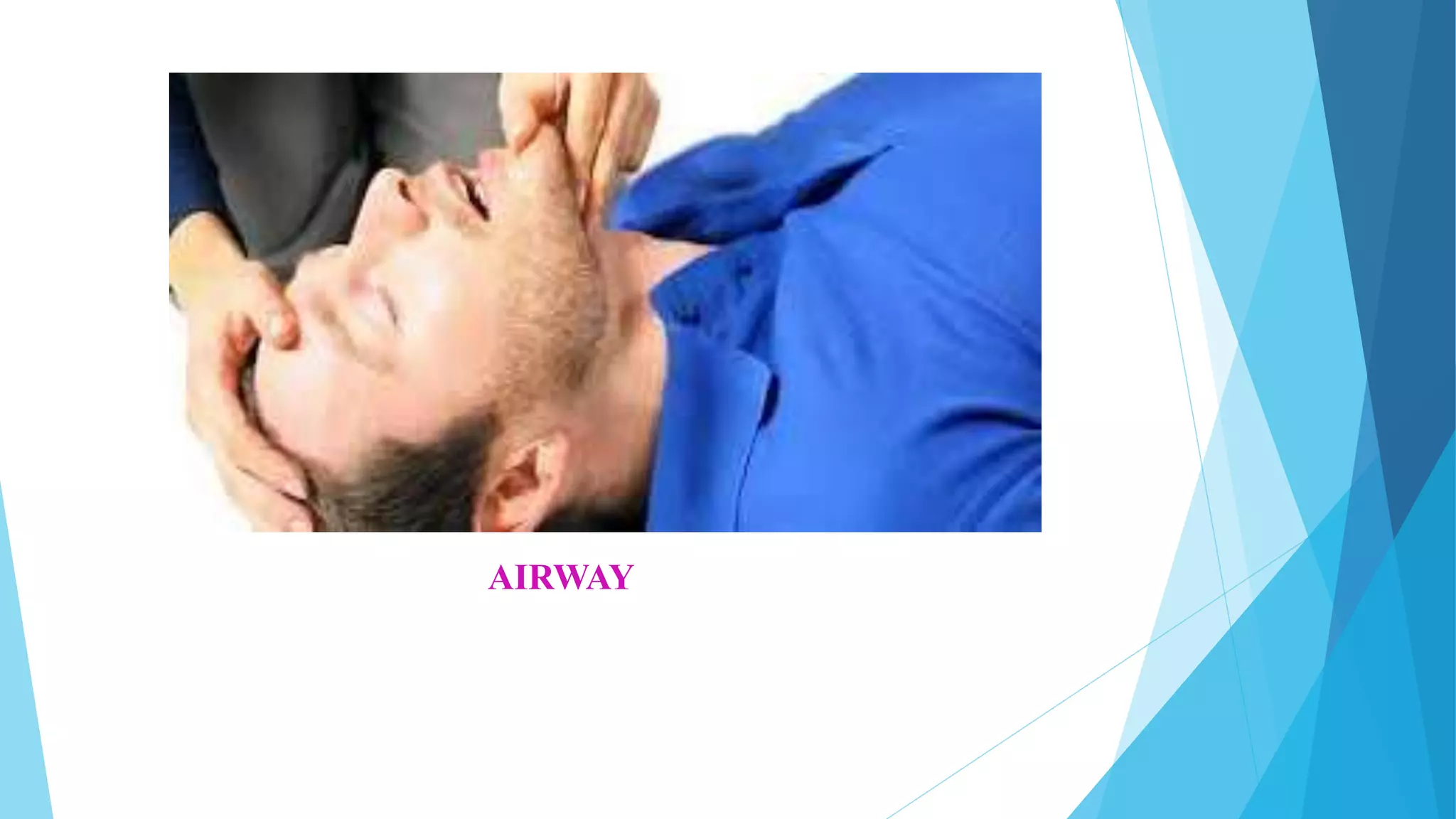
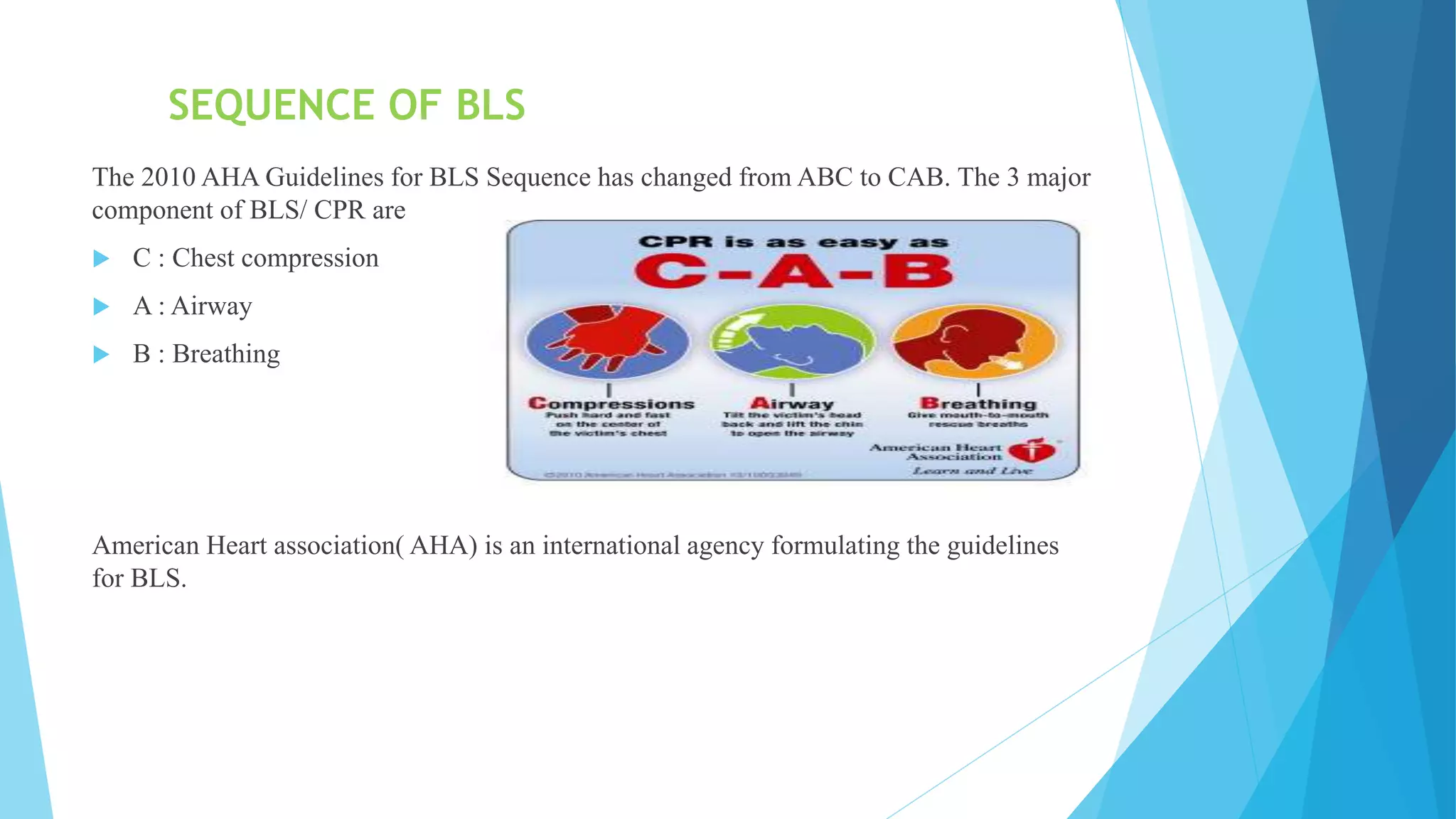
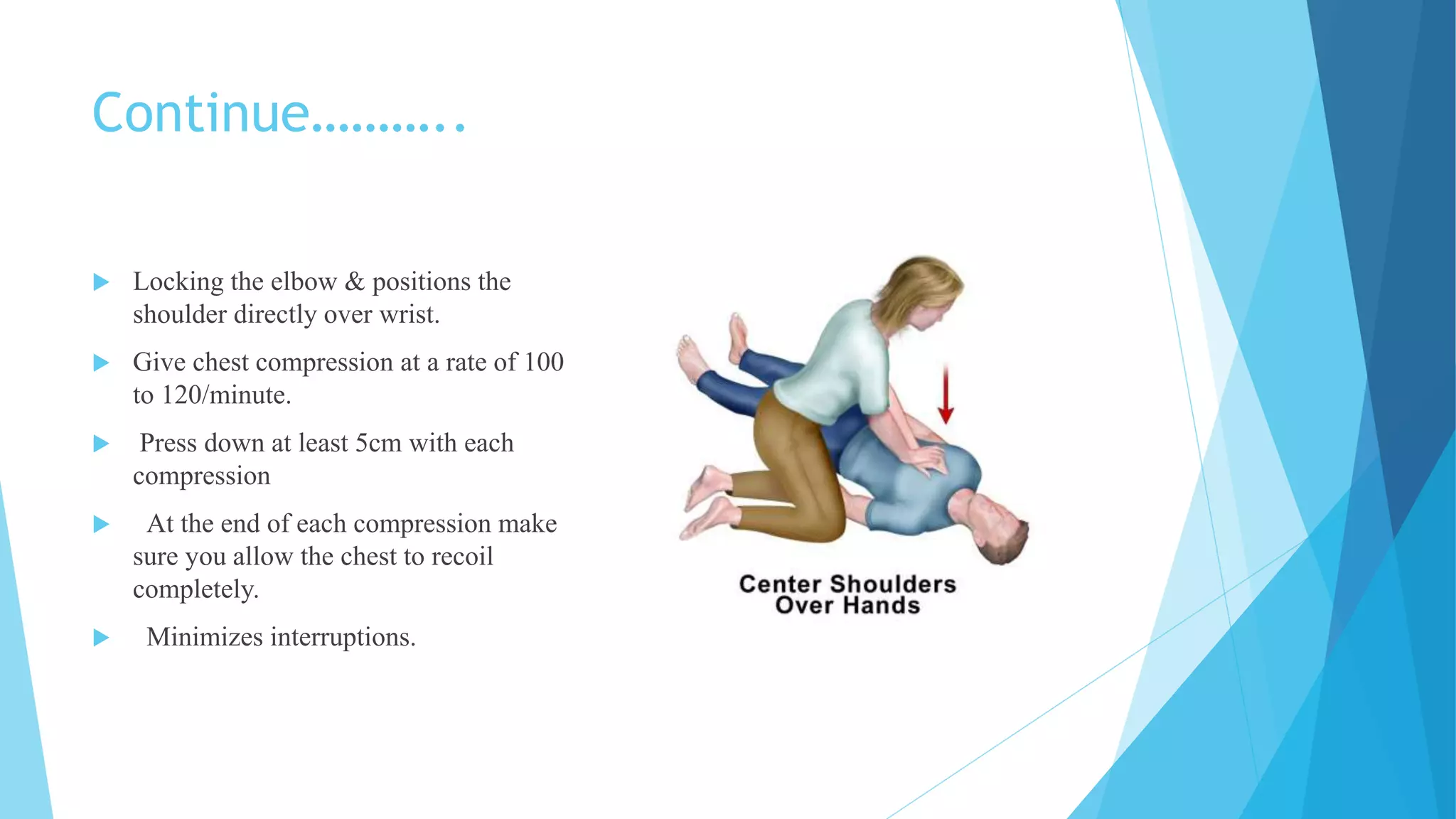
Cardiovascular diseases are the second leading cause of death, with cardiac arrest being responsible for 366,807 deaths per year in the US. Effective basic life support (BLS) provided immediately after cardiac arrest can double a victim's chance of survival. BLS involves chest compressions, opening the airway, and rescue breathing to sustain life until advanced medical treatment can restore normal heart function. It consists of five steps: assessing the scene and victim, checking for no pulse and breathing, beginning chest compressions, opening the airway, and giving rescue breaths. BLS is performed at a rate of 100-120 chest compressions per minute with complete chest recoil between compressions to promote circulation until emergency responders arrive.