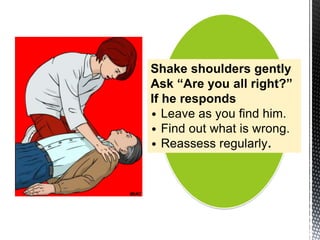
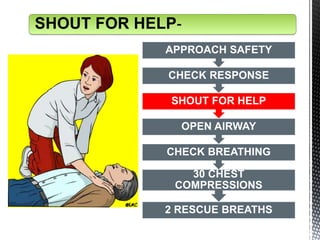
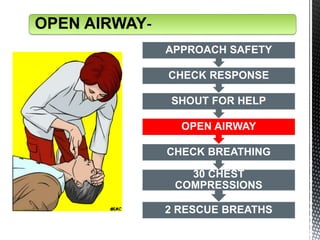
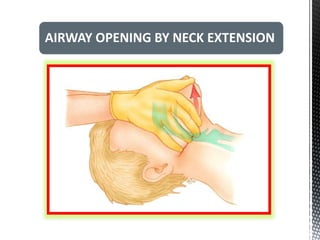
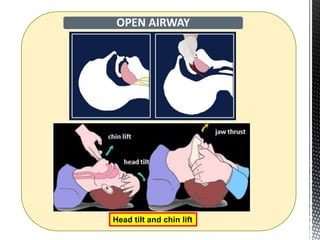
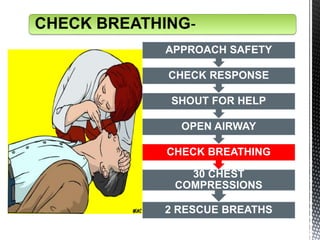
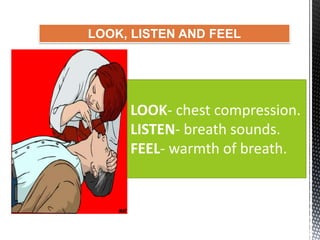
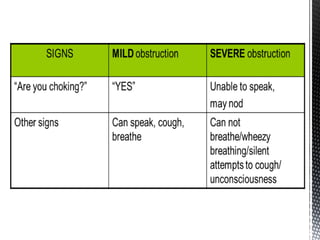
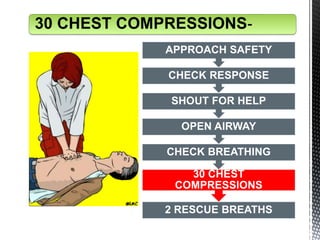
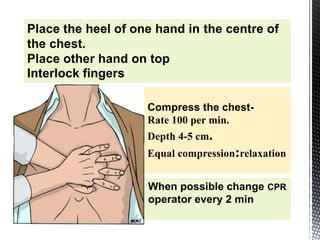
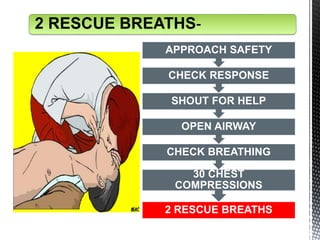
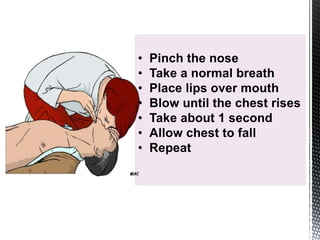
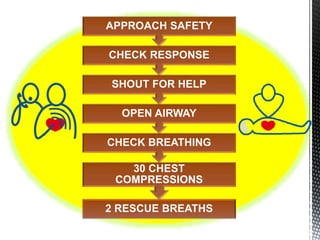
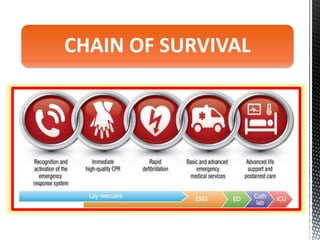
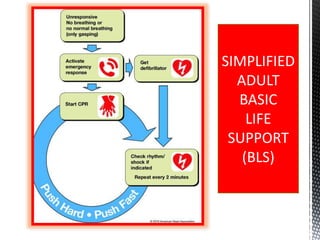
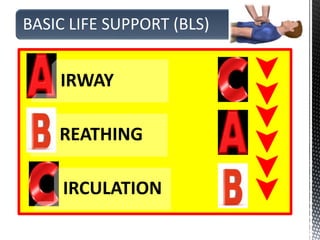
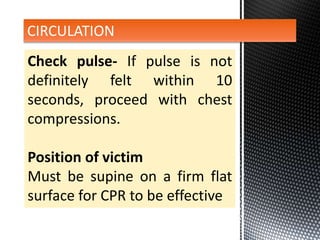
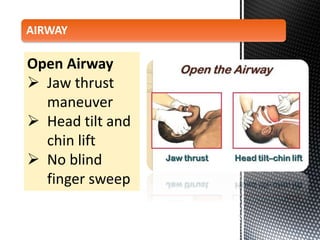
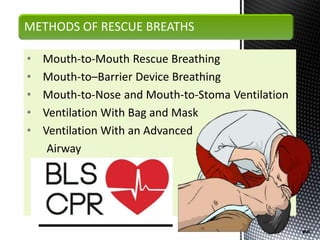
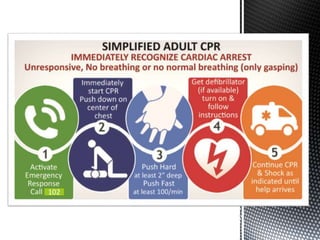
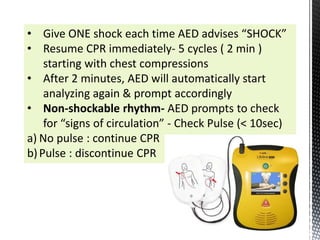
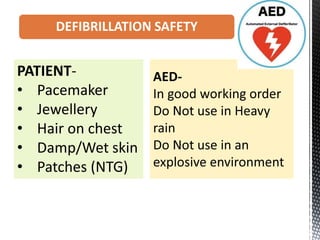
The document outlines the essential procedures and components involved in Basic Life Support (BLS), including the sequence of actions for CPR, the use of an Automated External Defibrillator (AED), and the importance of the chain of survival. It emphasizes the critical steps of checking for consciousness, breathing, and circulation, and the recommended compression-ventilation ratio during CPR. Additionally, it provides guidelines on safety and techniques for effective rescue breaths and compressions to improve patient outcomes during emergencies.





![Safety Of Self
Safety Of Patient
Movement of a
trauma victim only
when:-
absolutely
necessary [unstable
cervical spine]
injured spinal cord
ENSURE SAFETY- scene](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bls-190113181617/85/Basic-life-support-Cardi0-pulmonary-resuscitation-7-320.jpg)