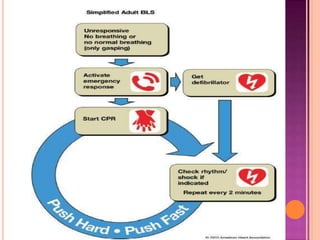
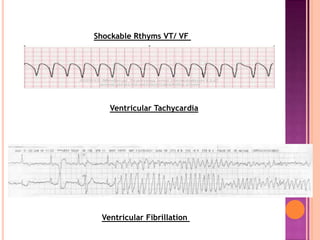
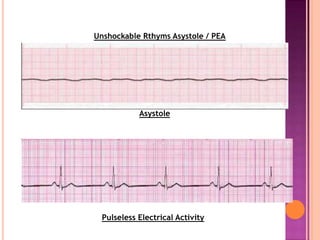
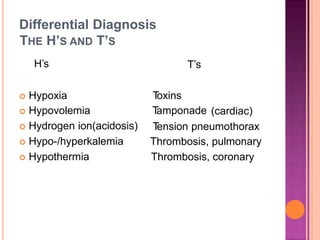
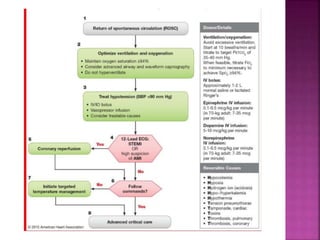
This document discusses Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). It begins by defining ACLS as a set of interventions for urgently treating cardiac arrest, stroke, and other emergencies, as well as the skills and knowledge to perform those interventions. The ACLS guidelines were first published in 1974 by the American Heart Association and are updated every five years. Basic life support forms the core foundation of ACLS, including chest compressions and use of automated external defibrillators. Only qualified healthcare providers can provide ACLS, as it requires skills like airway management, IV access, ECG interpretation, and emergency pharmacology. The document then outlines the ABCs of ACLS and protocols for ventilation, circulation, shockable and