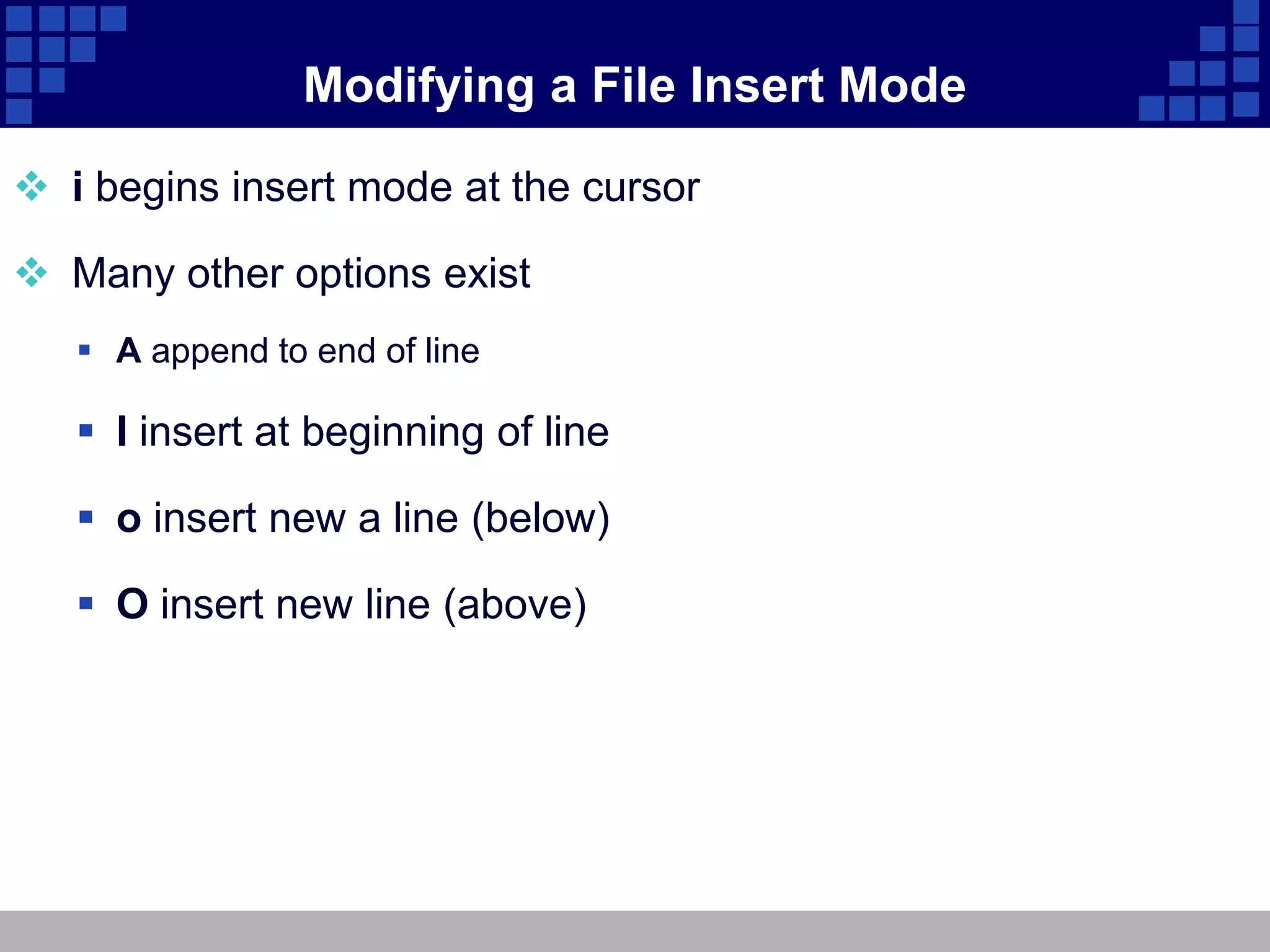
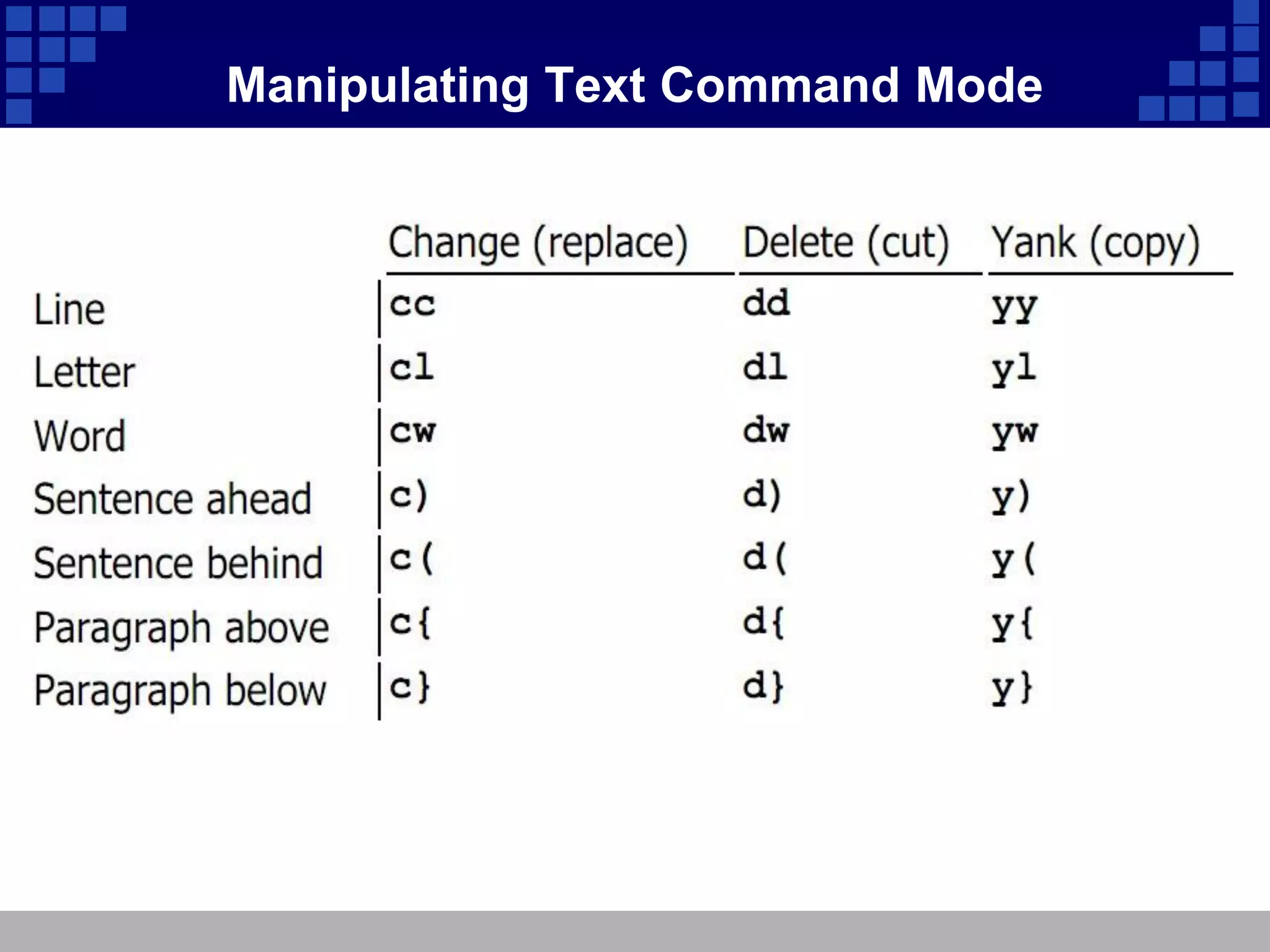
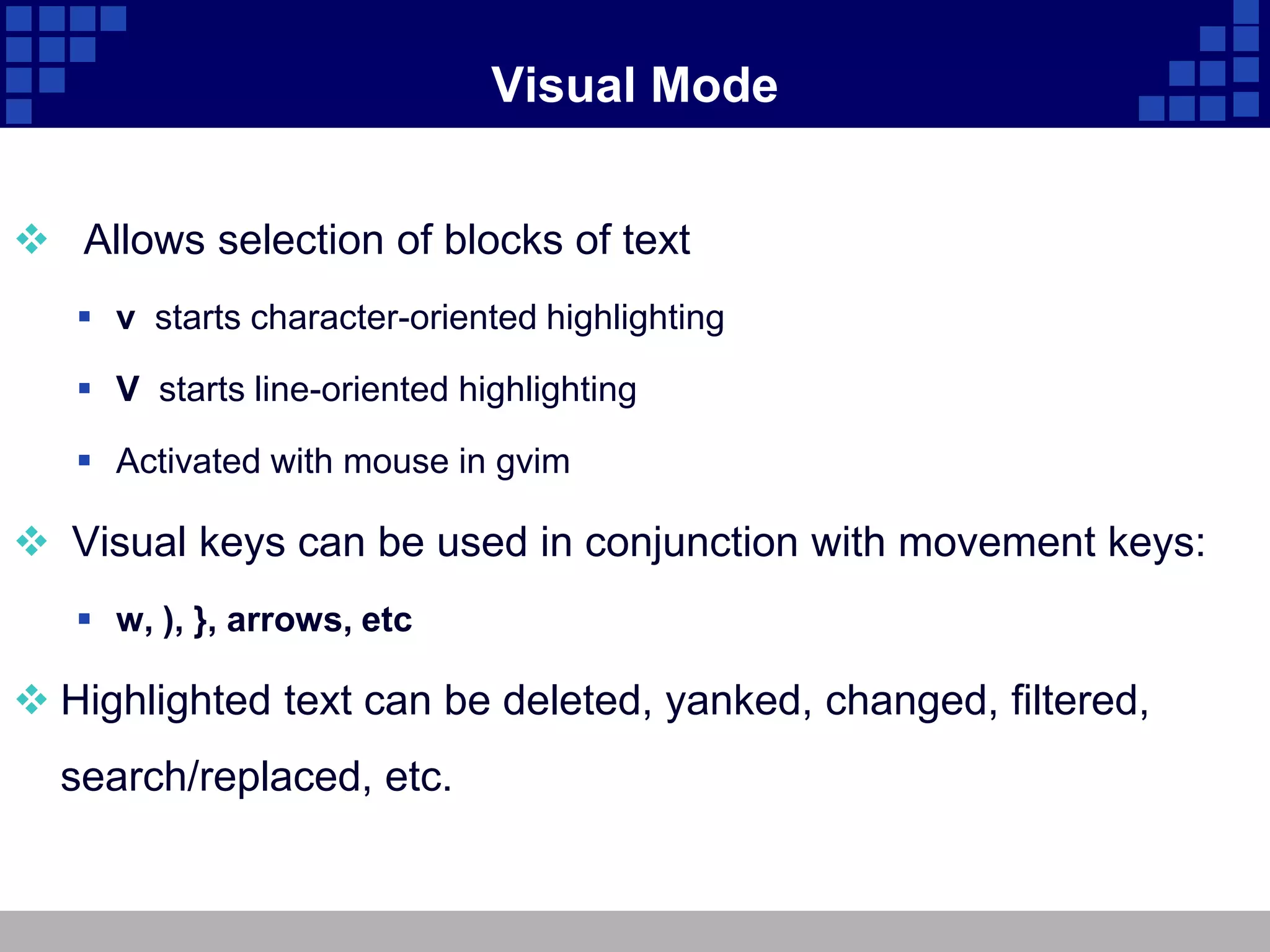
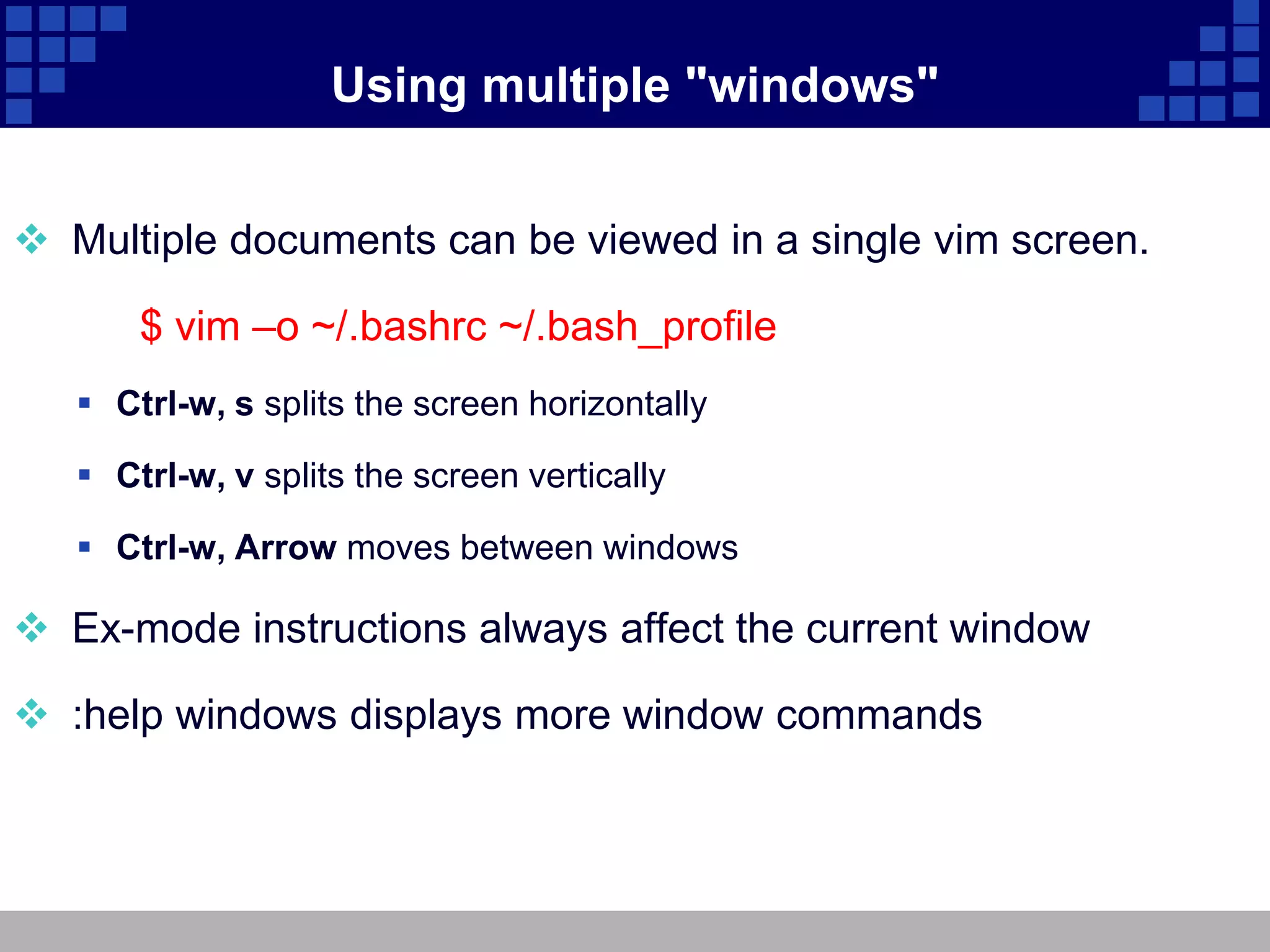
The document discusses vim, an advanced text editor that is a newer version of vi and provides graphical and command line interfaces, with details on how to open and modify files in insert mode, save and exit files in ex mode, move around and manipulate text in command mode, use search and replace, undo changes, work in visual mode, open multiple windows, configure vim settings, and find additional help resources.