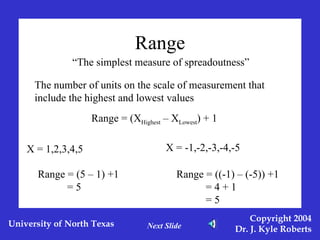
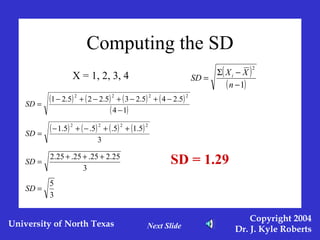
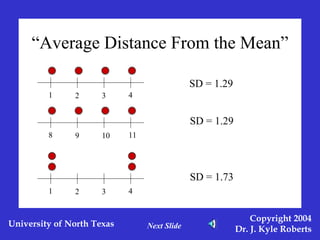
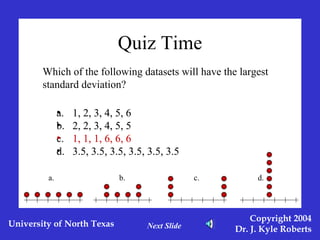
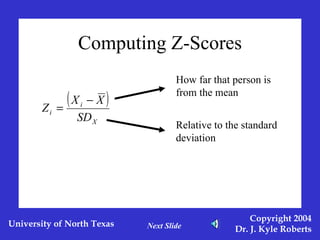
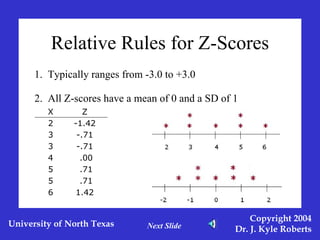
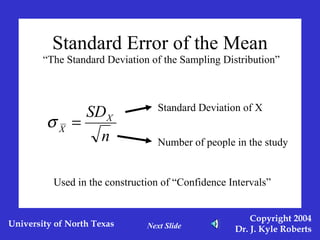
This document discusses different measures of spreadoutness in statistics, including range, standard deviation, z-scores, and standard error of the mean. It explains that range is the simplest measure but has limitations, while standard deviation measures how far scores are from the mean in the data's own units. Z-scores indicate an individual score's distance from the mean in units of standard deviations and allow comparison across data sets with different means and standard deviations. The standard error of the mean represents sampling error and is used to construct confidence intervals.