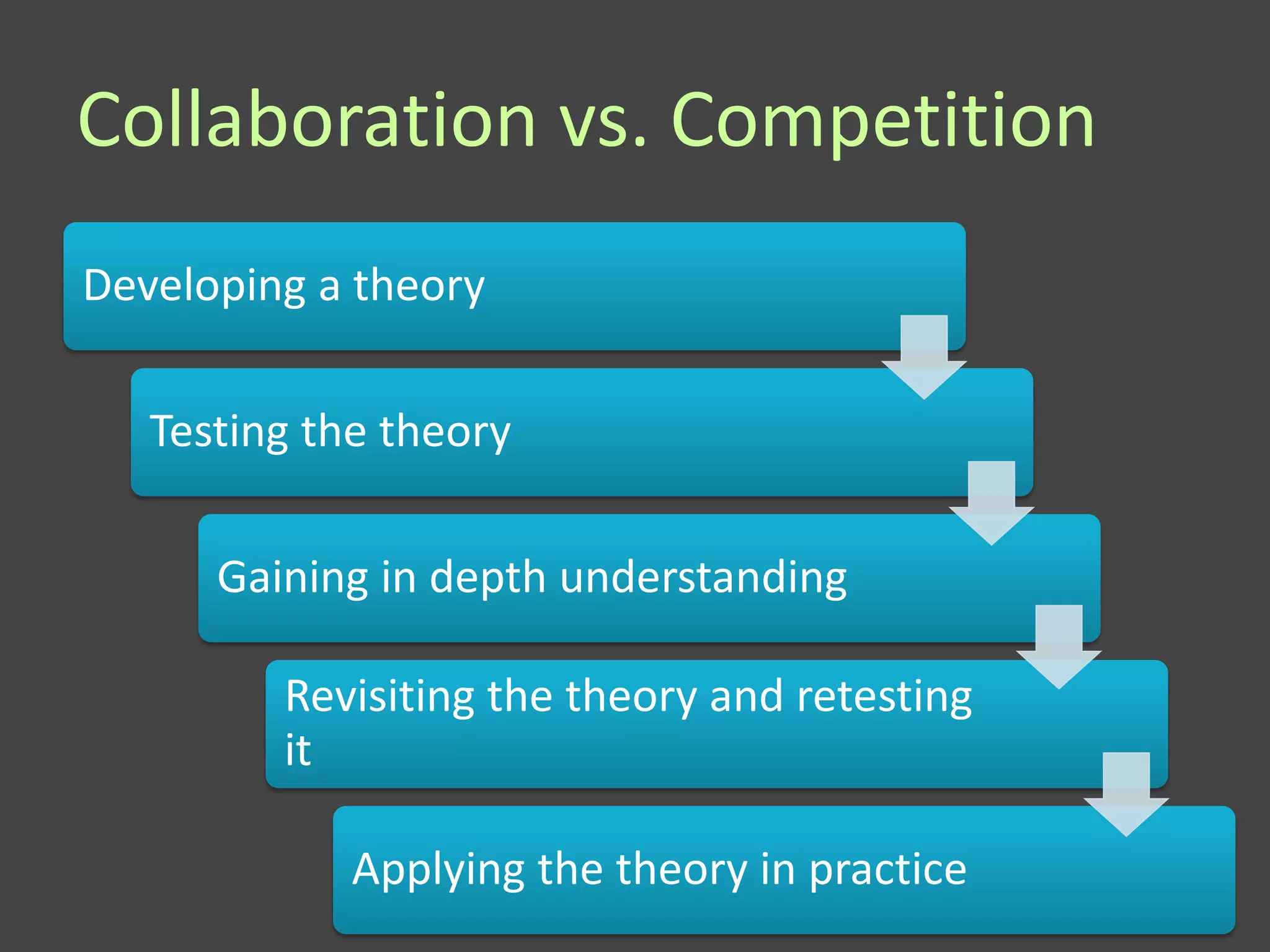
This document provides an overview of research methods, including qualitative and quantitative approaches. It discusses key aspects of developing a literature review, such as beginning with a broad topic and focusing on specific research questions. The document also compares different types of research (e.g. basic vs. applied), research paradigms (e.g. quantitative vs. qualitative), and study designs (e.g. experimental vs. case study). Fundamental questions about the nature of knowledge and how to choose an appropriate research method are explored.