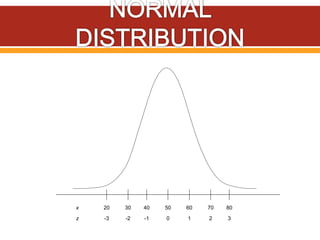
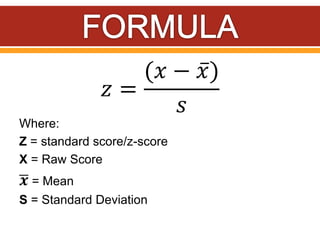
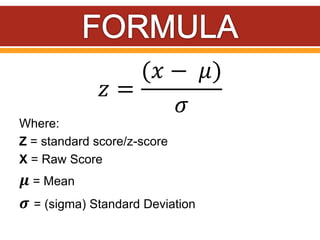
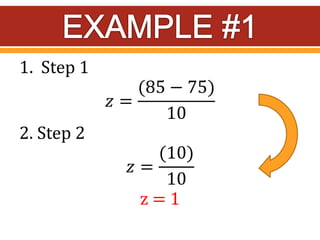
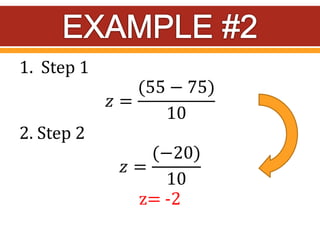
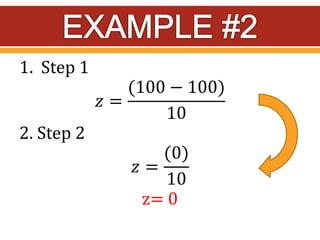
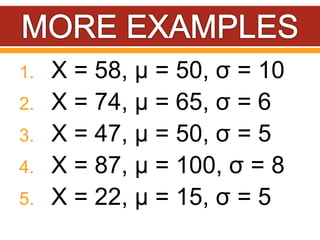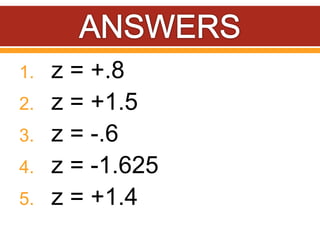Z-scores, also called standard scores, measure how many standard deviations a raw score is above or below the mean of its distribution. A z-score indicates where a particular score lies in relation to all other scores in the distribution. To calculate a z-score, the raw score is subtracted from the mean and divided by the standard deviation of the distribution. Z-scores can be positive, negative, or zero, depending on whether the raw score is above, below, or equal to the mean. Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating z-scores from raw scores, means, and standard deviations.