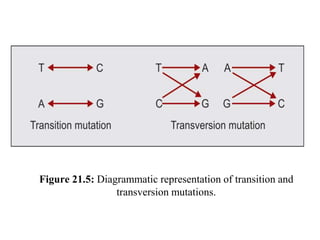
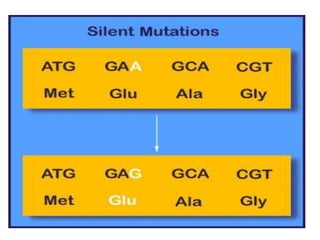
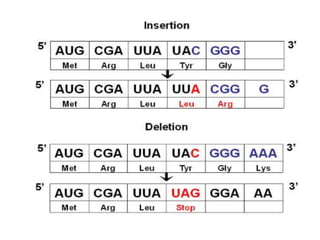
Mutations are permanent changes in the DNA sequence that can be caused by errors during DNA replication, environmental factors like radiation and chemicals, or spontaneous changes. Mutations in germ cells can cause inherited diseases while those in somatic cells can lead to cancer. There are several types of mutations, including base substitutions, deletions, insertions, and frameshift mutations. Mutations can have different effects, such as being lethal, silent, beneficial, or carcinogenic by altering regulatory mechanisms and causing uncontrolled cell division.