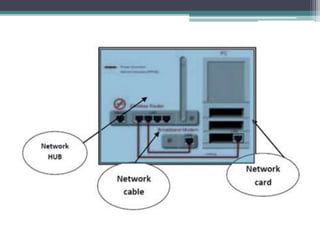
There are several types of computer errors that can occur at different stages of booting up or using a computer. These include hardware errors like no video output, software errors from corrupted files, and operating system errors. To diagnose issues, one should check connections, review error messages, update drivers, scan for malware, and test in safe mode. Common solutions involve reseating or replacing hardware, updating software, and ensuring proper ventilation and power supply.