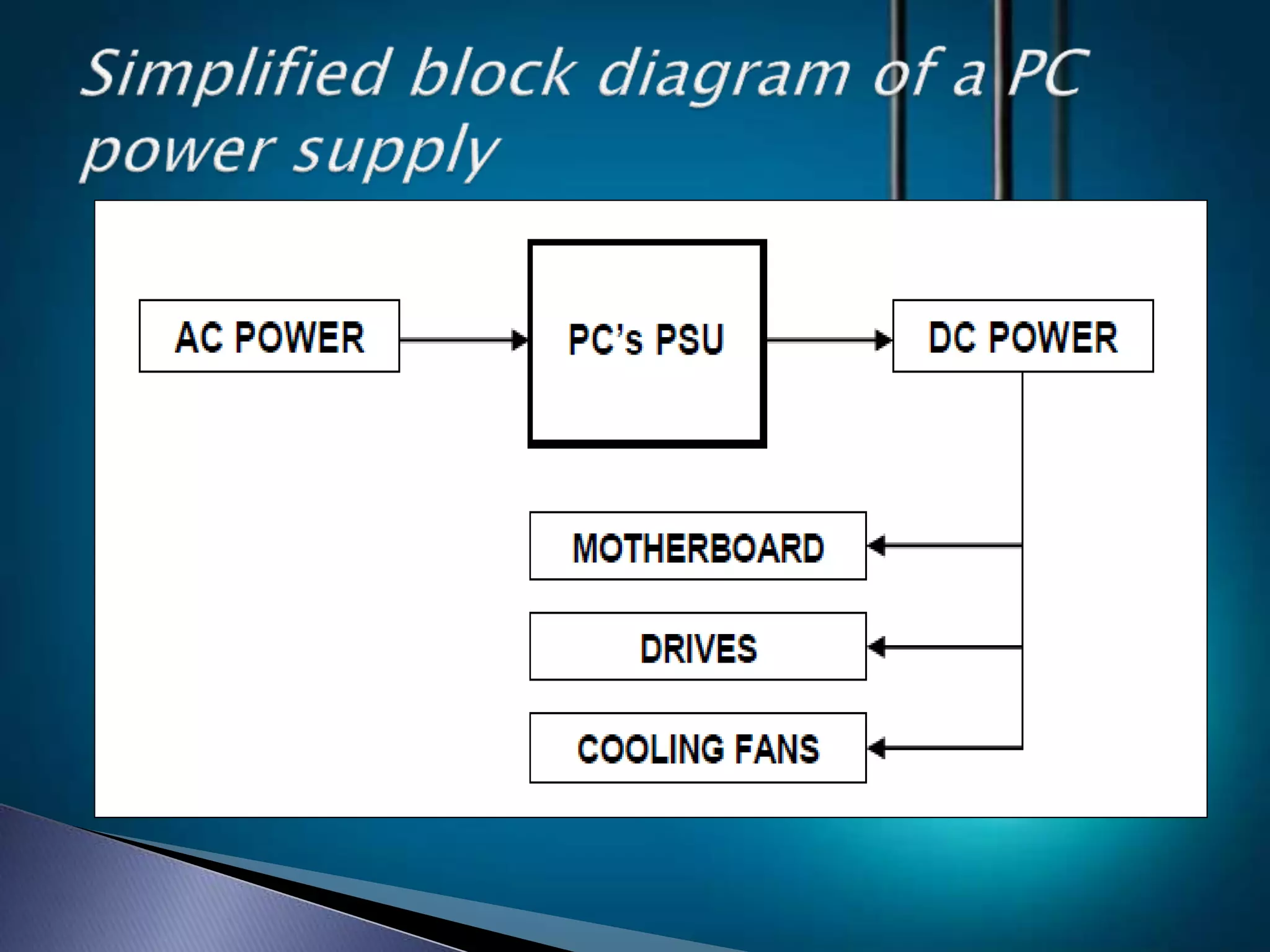
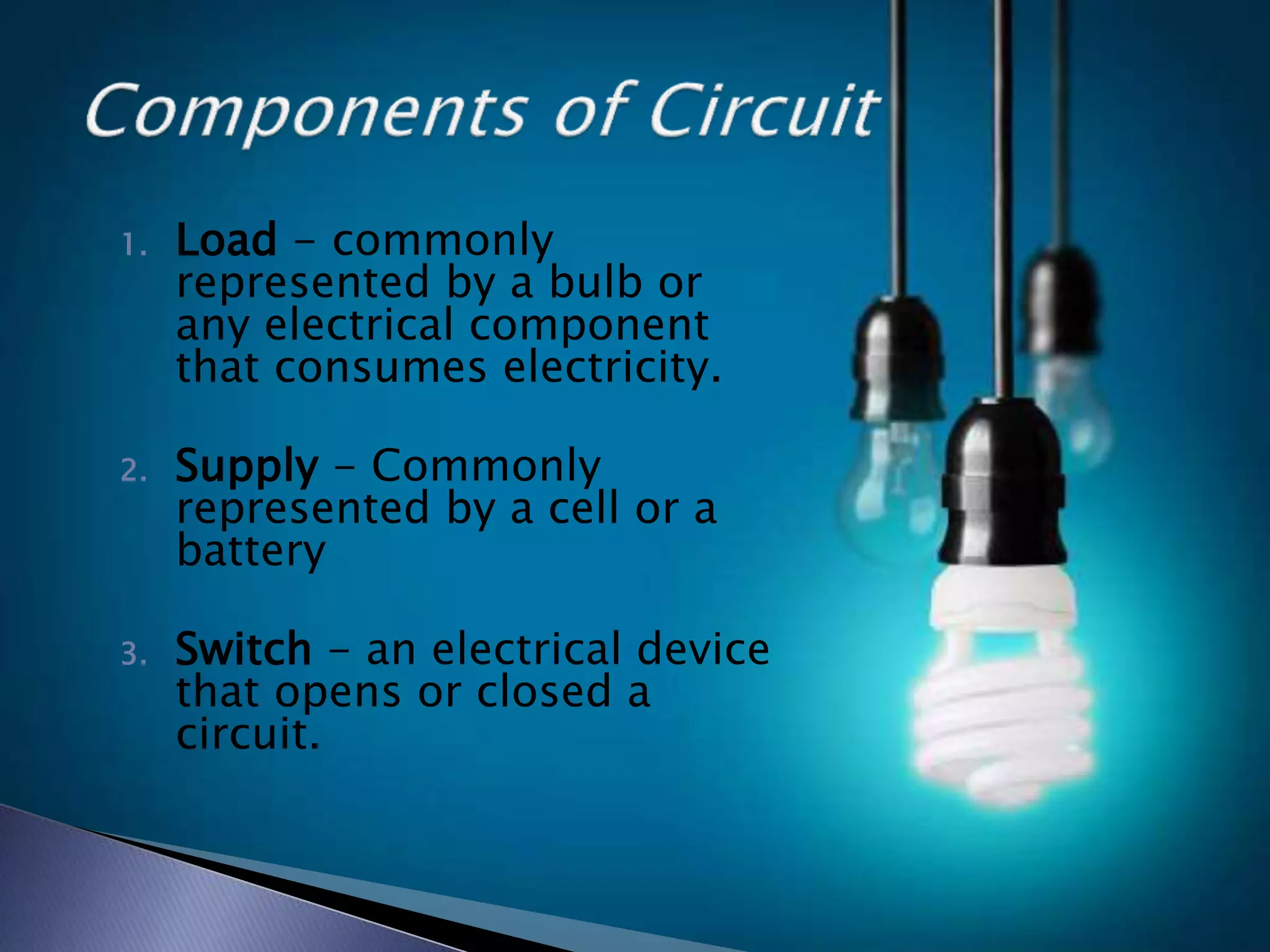
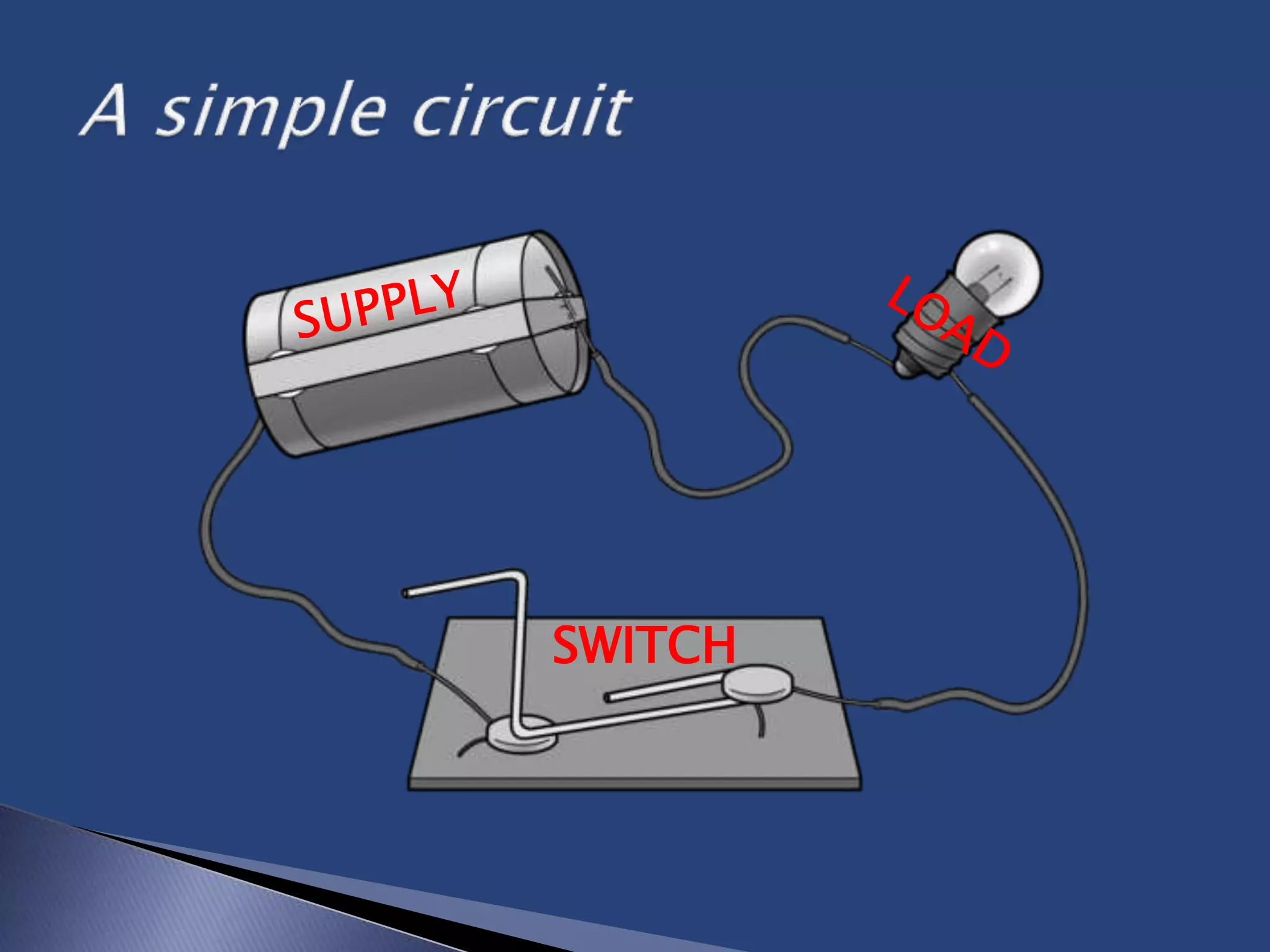
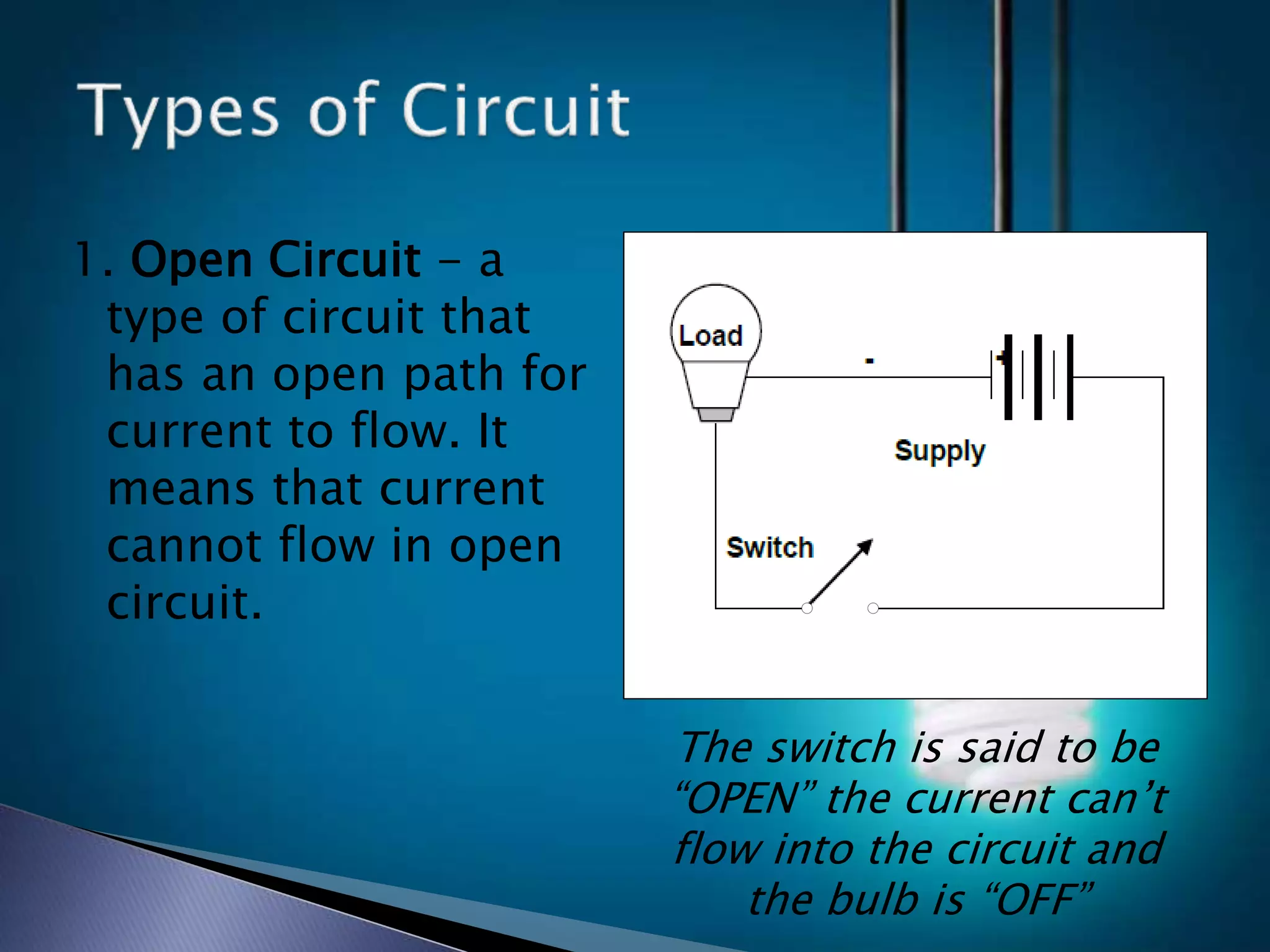
The document discusses the basic concepts of electricity including direct current (DC), alternating current (AC), voltage, resistance, and circuits. It explains that DC flows in one direction while AC periodically reverses direction, and that AC is easier to transmit over long distances due to transformer capabilities. The basic components of an electric circuit are also defined as the load, supply, and switch.