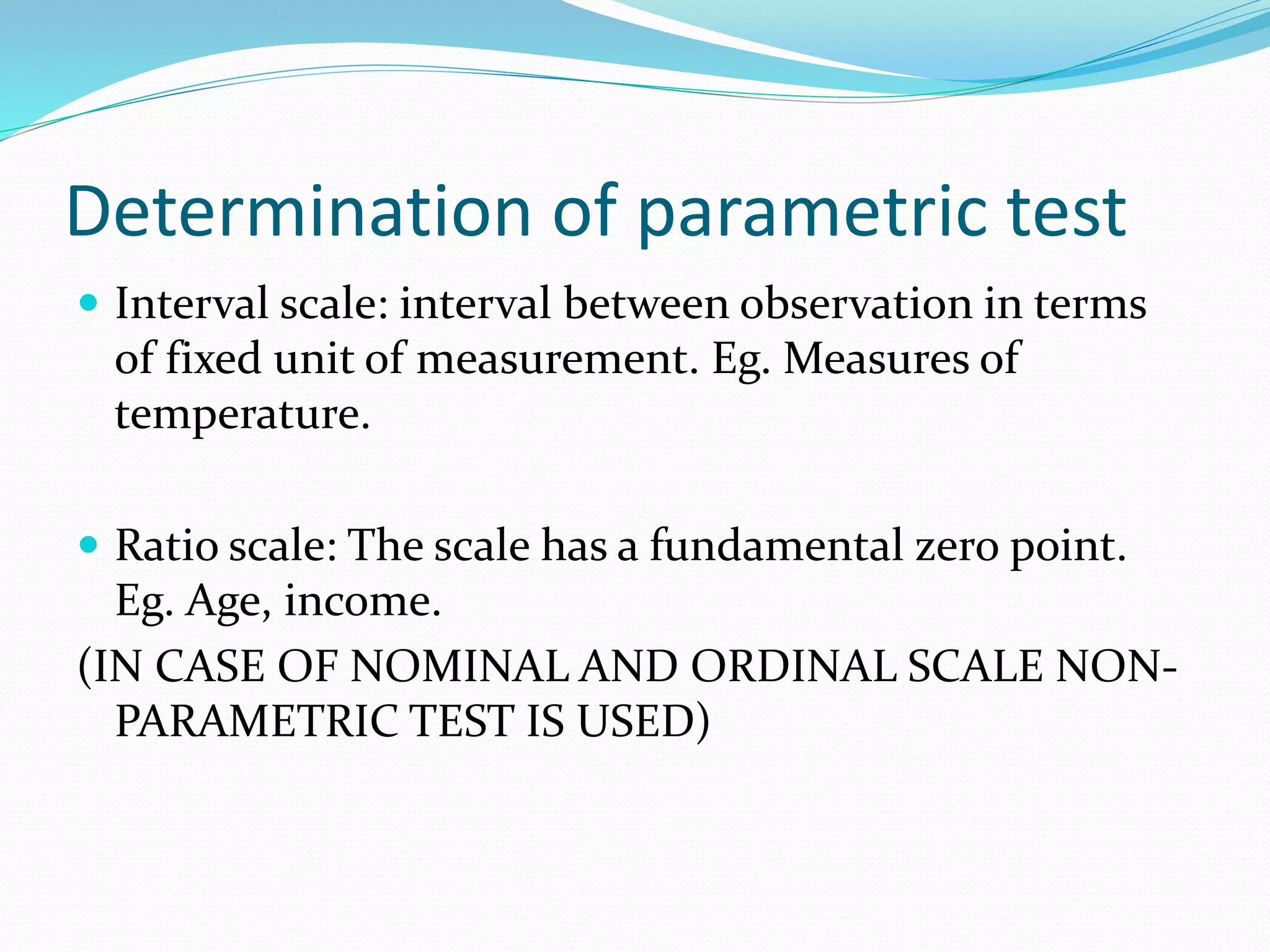
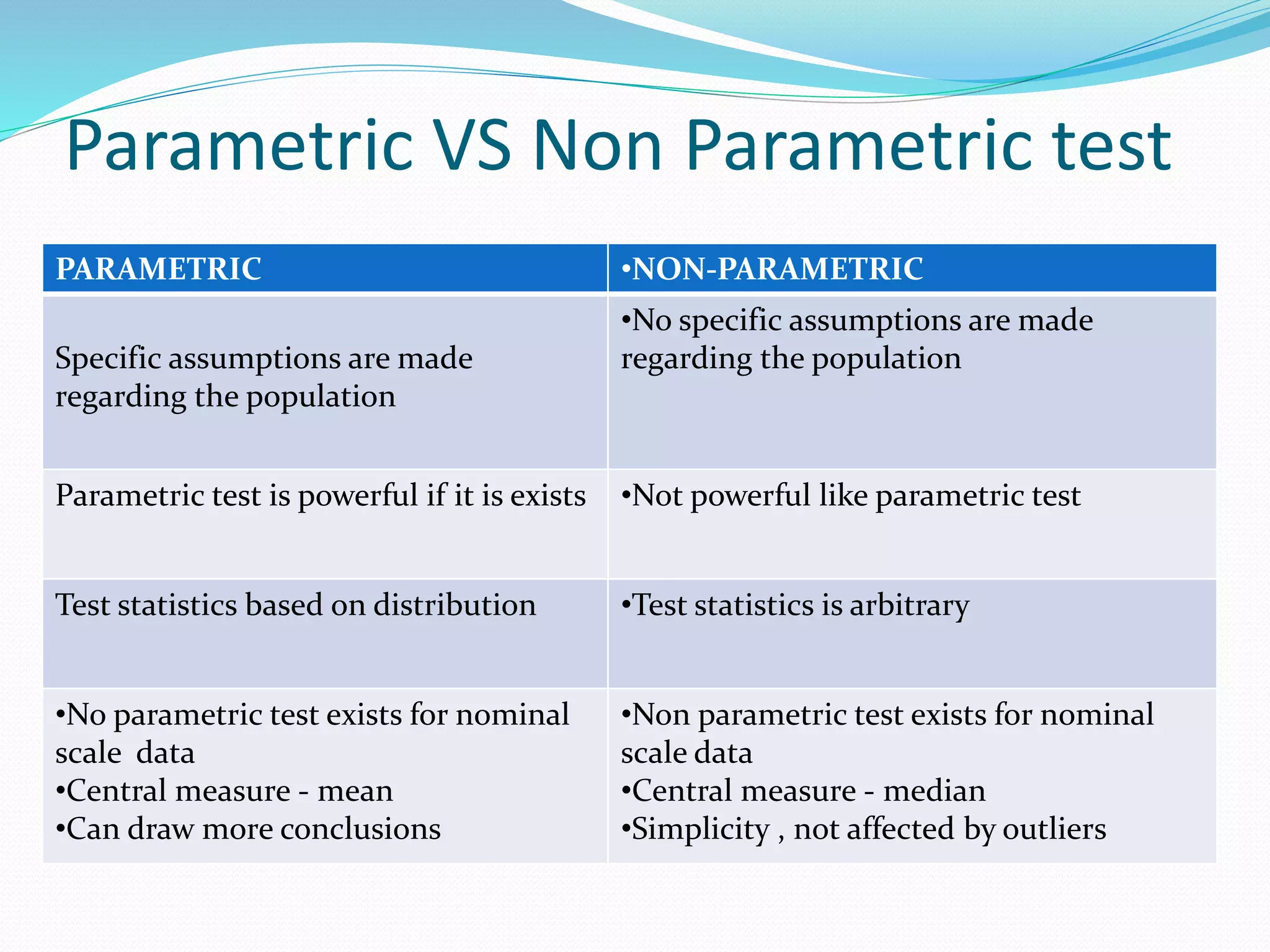
This document provides an introduction to parametric tests in statistics. It defines a parametric test as a statistical test that makes specific assumptions about the population parameter. For a test to be considered parametric, the data must meet four conditions: it must be on an interval or ratio scale, subjects must be randomly selected, and the data must be normally distributed. Examples of parametric tests include t-tests, ANOVA, and z-tests. Parametric tests are more powerful than non-parametric tests if their assumptions are met, but non-parametric tests can be used when the data does not meet parametric assumptions, such as with nominal scale data.