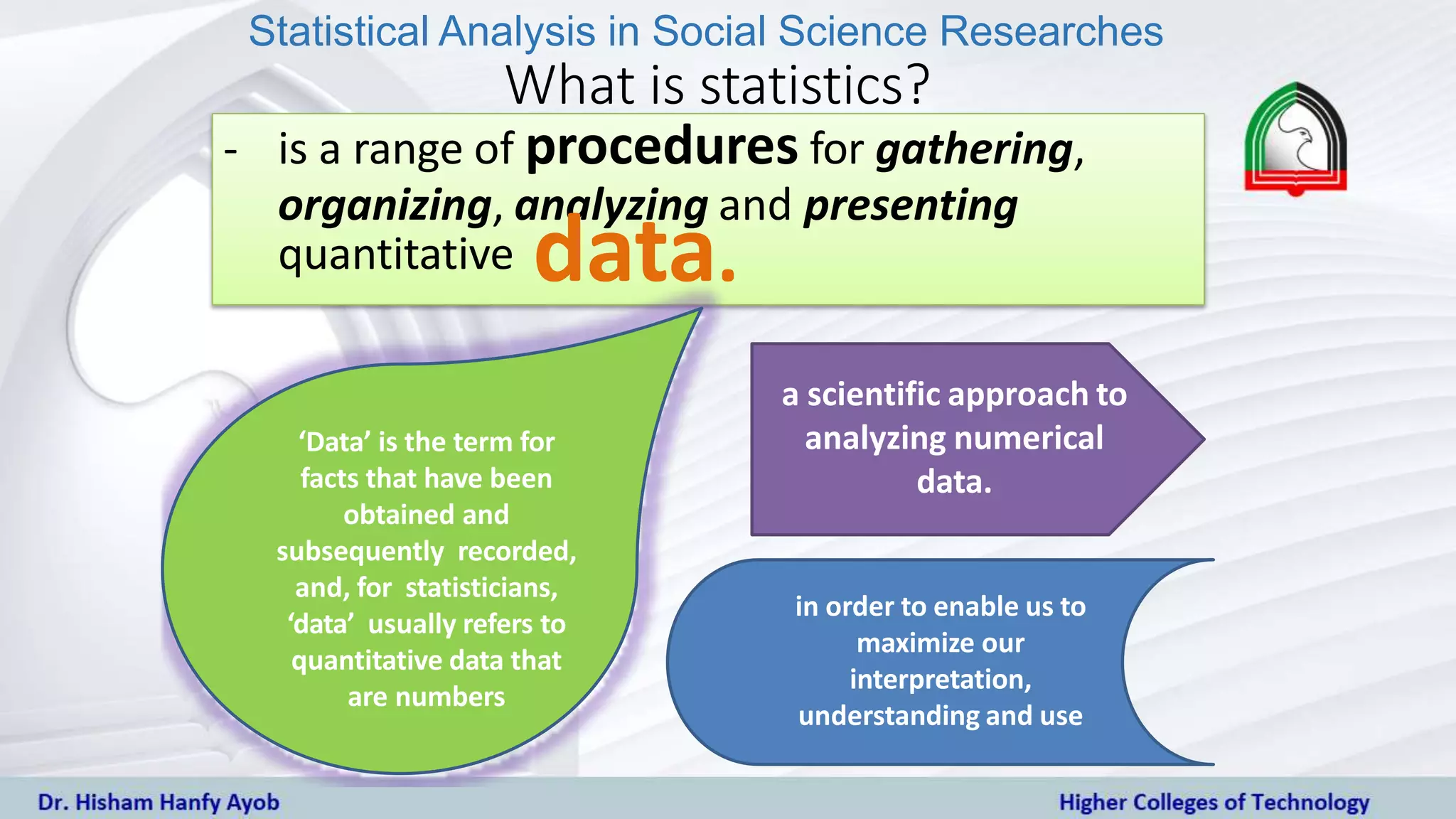
Statistical analysis is used in social science research to analyze quantitative data using methods like descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and exploratory statistics. Descriptive statistics summarize and describe data through measures like frequency, central tendency, and dispersion. Inferential statistics determine significant relationships between variables by testing hypotheses using techniques like chi-square tests, correlation, and regression. Exploratory statistics involve cluster analysis to develop groupings within the data. Statistical analysis helps measure, examine, predict, classify patterns in data, and draw conclusions from samples to generalize to populations.