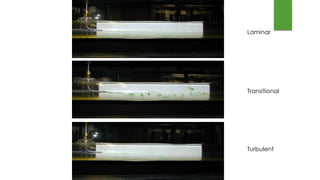
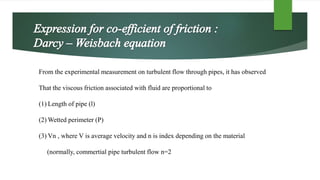
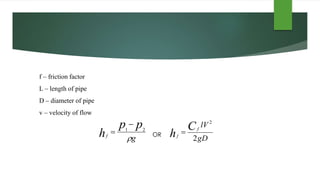
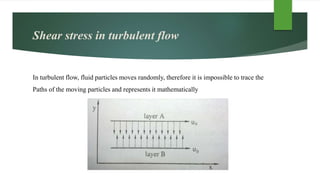
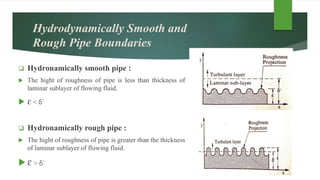
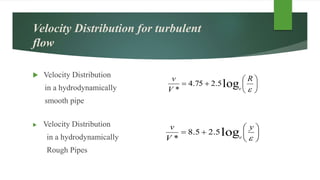
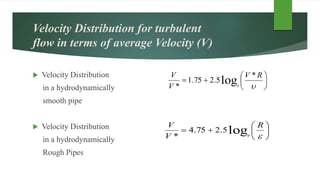
This document discusses turbulent flow and provides definitions and equations related to turbulent flow characteristics. It defines laminar and turbulent flow, noting that turbulent flow involves irregular random movement transverse to the main flow. The type of flow depends on the Reynolds number, with laminar flow below 2000 and turbulent flow above. Turbulent flow magnitude and intensity are defined using root mean square equations. Equations are also provided for friction factor in turbulent pipe flow involving length, diameter, velocity. Prandtl's mixing length theory is described for modeling turbulent shear stress. Boundaries can be hydrodynamically smooth or rough depending on roughness height compared to the laminar sublayer thickness. Velocity distributions in smooth and rough pipes are shown using logarithmic equations involving thickness and