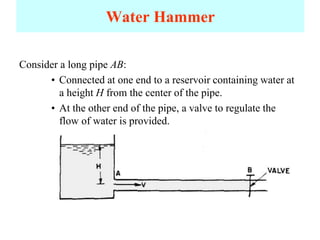
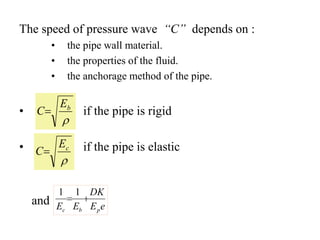
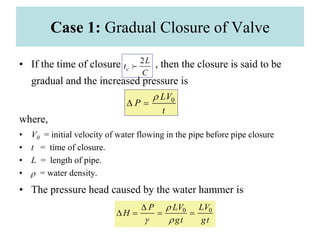
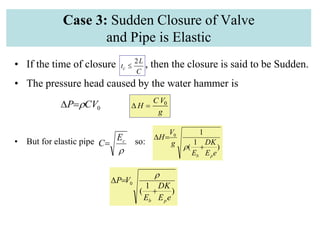
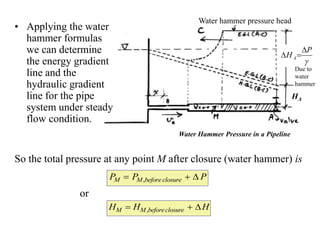
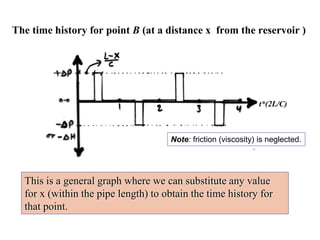
This document discusses unsteady flow in pipes, also known as water hammer phenomenon. When a valve closes suddenly in a pipeline, it can cause a pressure wave that travels through the pipe at the speed of sound. This pressure wave can exceed the normal pressure in the pipe and damage the pipe walls. The document analyzes water hammer for different scenarios including gradual vs sudden valve closure and rigid vs elastic pipes. It provides formulas to calculate the pressure rise, stresses in the pipe wall, and pressure wave time histories at different points in the pipe. An example problem is also included to demonstrate calculating these values.