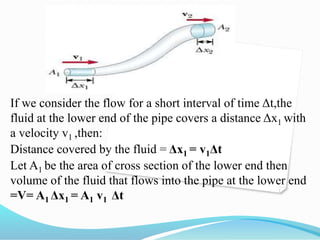
This document discusses the continuity equation in fluid mechanics. It defines the continuity equation as the product of cross-sectional area and fluid speed being constant at any point along a pipe. This constant product equals the volume flow rate. The document then derives the continuity equation mathematically by considering the mass flow rate at the inlet and outlet of a pipe with varying cross-sectional areas but steady, incompressible flow. It provides an example calculation and solution for water flow rates and velocities through pipes of different diameters.