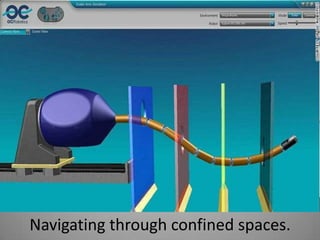
The document discusses the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in power plants, highlighting its applications in thermal, hydal, and nuclear power plants. It emphasizes mobile monitoring and robotic maintenance as solutions for efficient plant operation and safety, including the use of specialized robots like line scouts and snake-arm robots for inspections and repairs. AI technologies are set to enhance monitoring and maintenance practices in hazardous environments, particularly in the nuclear sector.