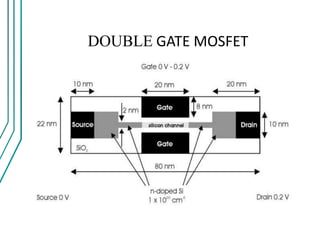
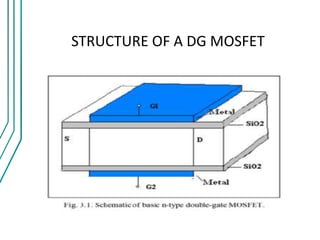
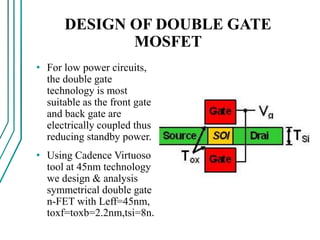
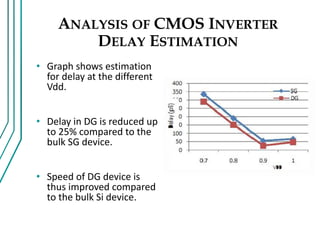
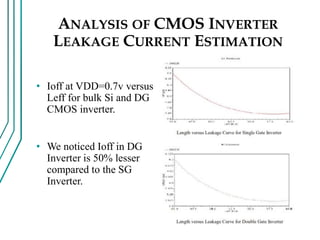
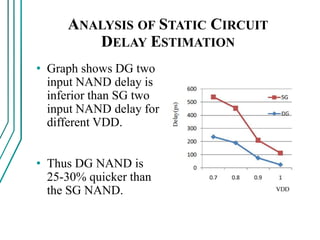
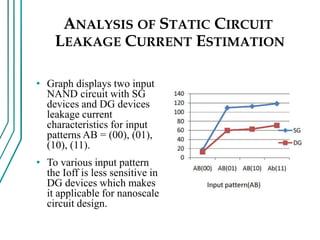
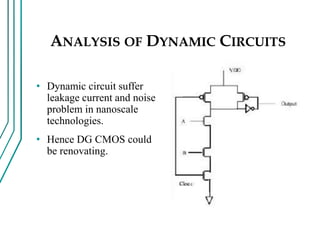
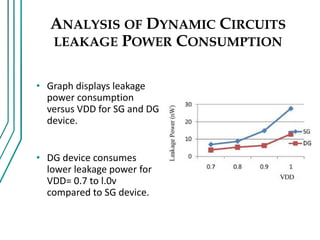
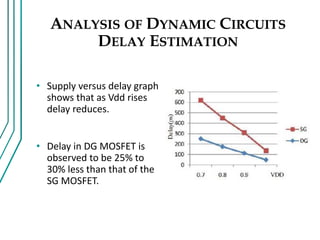
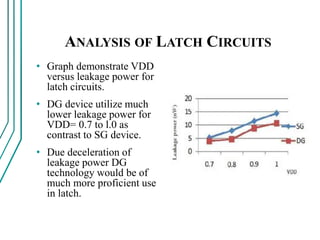
The document compares double gate MOSFETs to single gate MOSFETs. Double gate MOSFETs reduce leakage current and delay compared to single gate by controlling the silicon channel more efficiently with two gates. This improves short channel effects and leads to higher currents. Double gate MOSFETs are suitable for low power and high performance applications due to their reduced leakage current and improved device characteristics like reduced short channel effects and improved current driving capability.