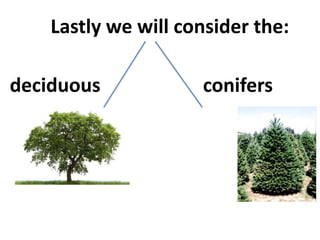
The document discusses two main types of trees: deciduous and conifers. Deciduous trees have broad leaves that lose water and change color in the fall, while coniferous trees grow in a triangular shape with needle-like leaves that reduce water loss and are adapted to cold environments. Both types of trees have unique reproductive methods, with deciduous trees producing seeds within fruits and conifers using cones to shelter their seeds.