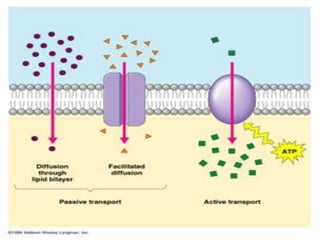
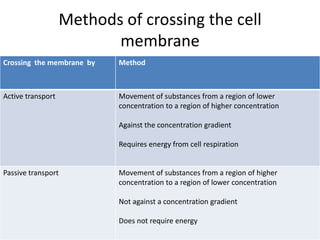
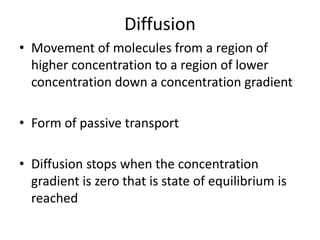
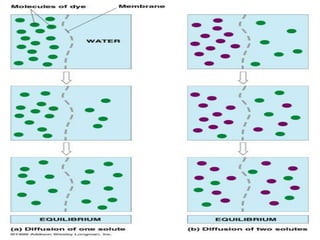
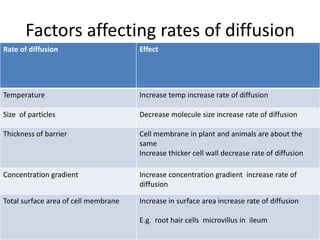
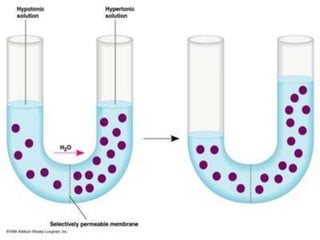
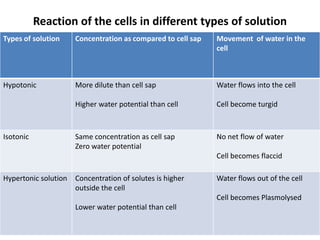
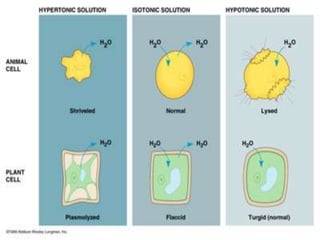
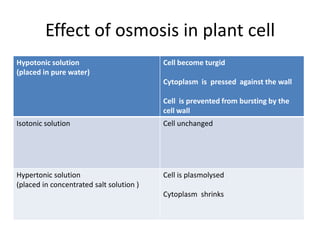
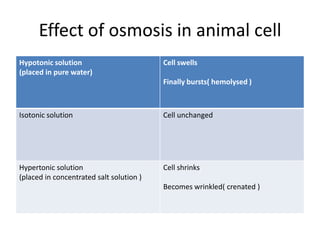
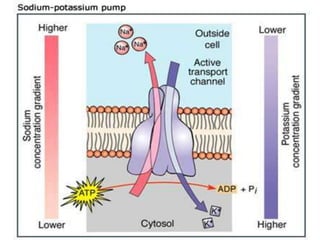
This document discusses diffusion, osmosis, and active transport as methods for substances to cross cell membranes. It defines diffusion as the passive movement of molecules down a concentration gradient not requiring energy. Osmosis is defined as the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a lower to higher water potential. Active transport moves substances against a concentration gradient and requires energy. The document describes the process and importance of diffusion, osmosis, and active transport and factors that affect their rates.