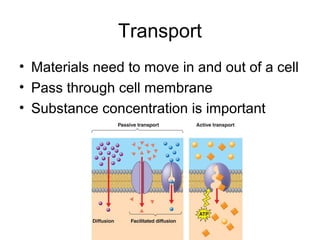
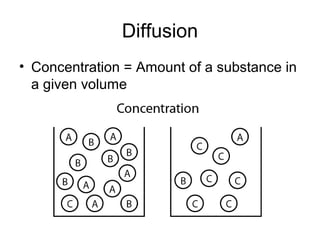
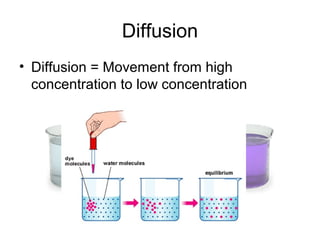
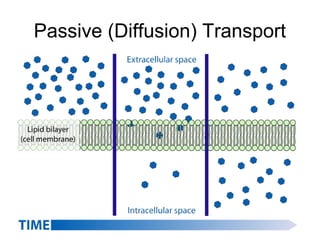
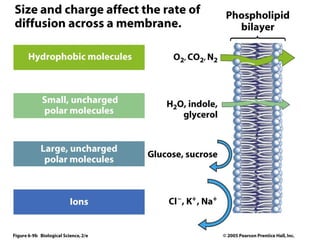
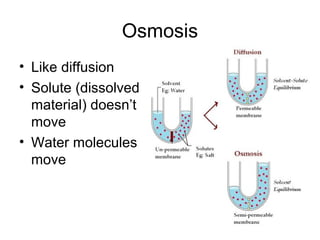
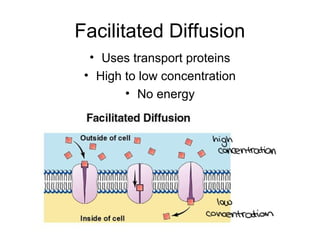
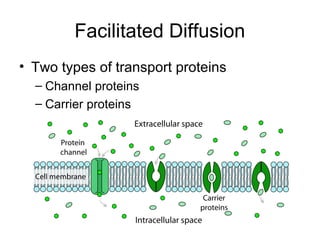
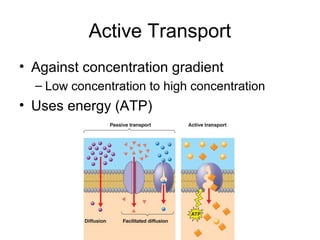
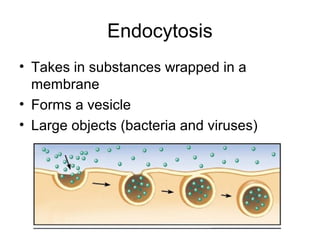
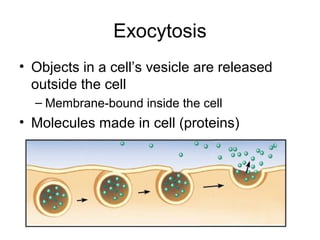
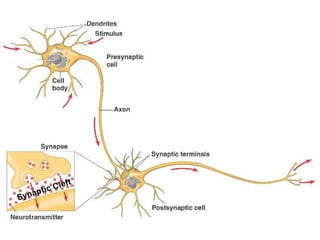
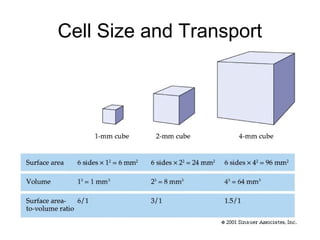
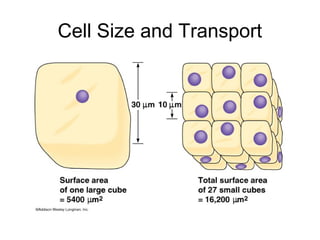
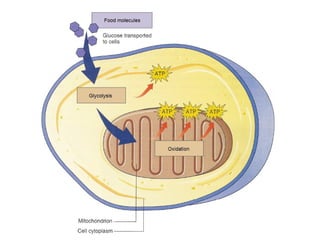
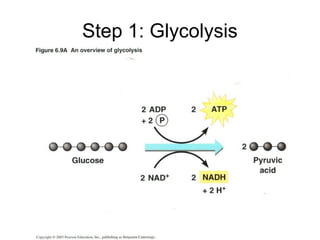
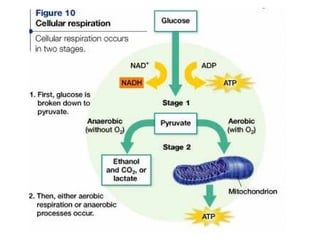
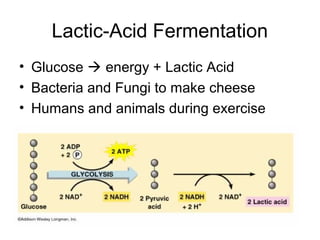
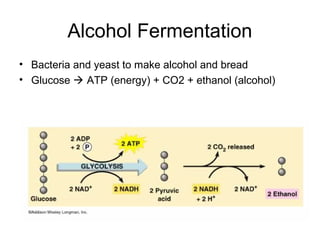
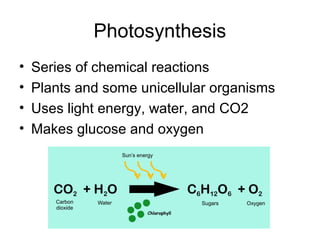
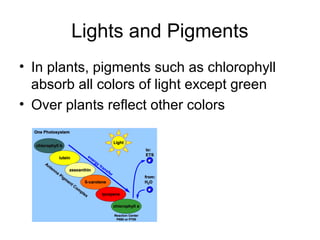
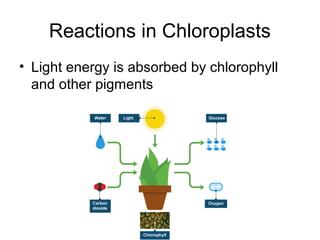
Cellular transport involves the passive and active movement of substances across the cell membrane. Passive transport includes diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis, which move substances down their concentration gradient without energy expenditure. Active transport moves substances against their gradient by using cellular energy in the form of ATP. Endocytosis and exocytosis are mechanisms for cells to take in and release larger particles by engulfing and vesiculating parts of the membrane. Cell size and surface area have an important relationship to transport, as larger surface area is needed to support substance movement into and out of a cell.