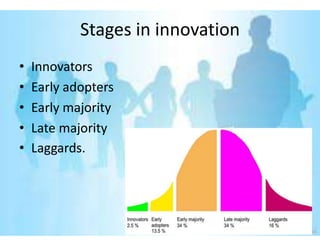
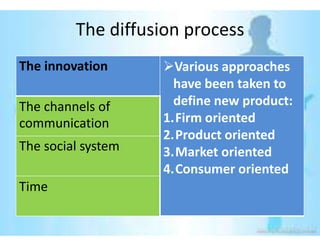
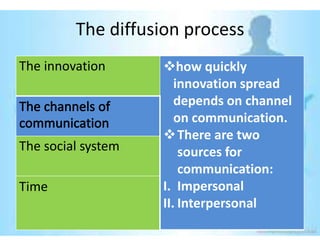
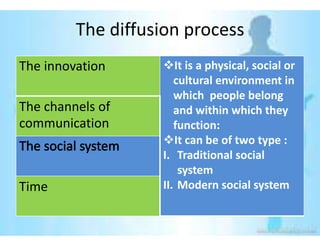
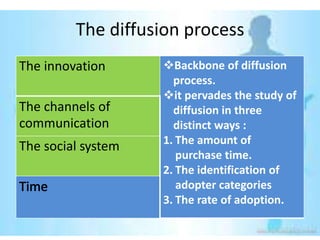
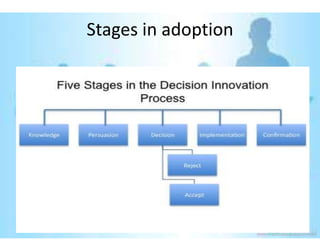
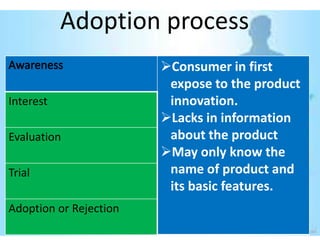
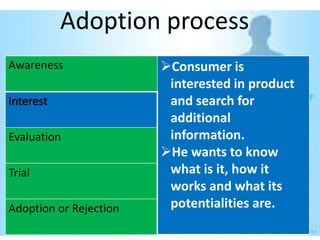
This document provides an overview of the diffusion of innovation theory and consumer adoption processes. It discusses key concepts like the stages of innovation adoption (innovators, early adopters, etc.), characteristics that influence diffusion, and the awareness-interest-evaluation-trial-adoption consumer decision process. It also profiles different types of early adopters like opinion leaders, market mavens, change leaders, and technophiles who influence wider adoption. The document concludes by noting applications for marketing research, new product development, and product reviews.