The document discusses various mechanisms of transport across cell membranes:
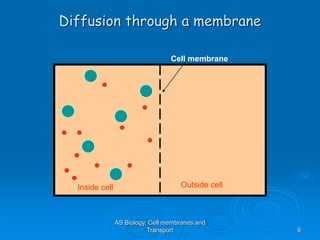
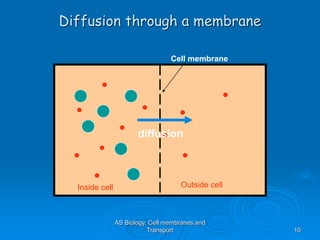
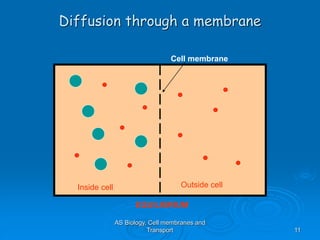
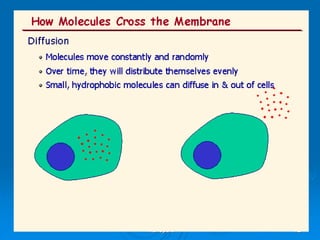
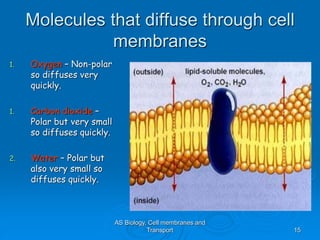
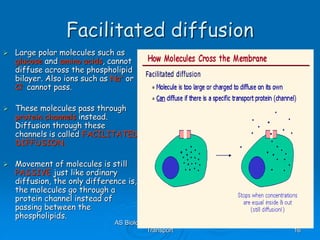
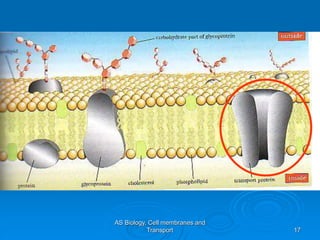
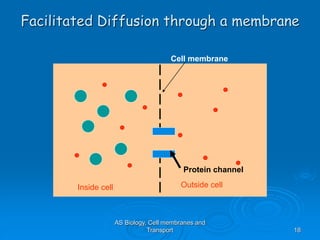
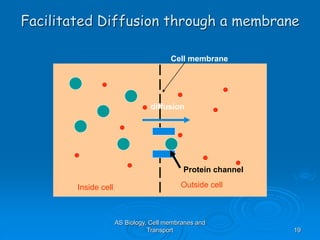
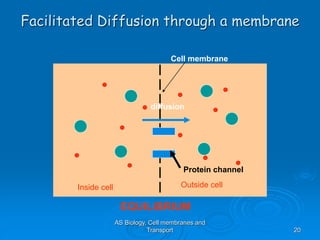
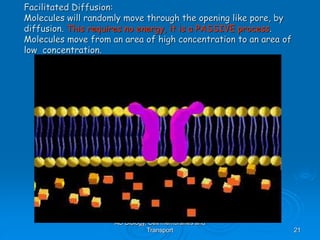
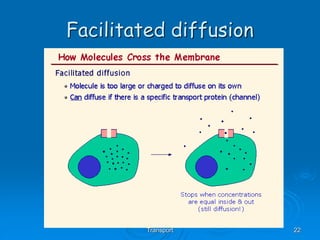
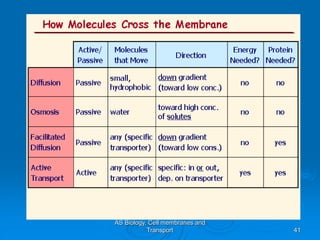
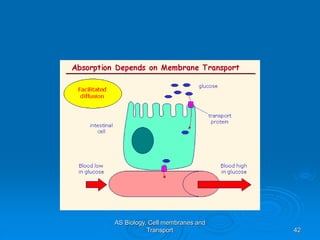
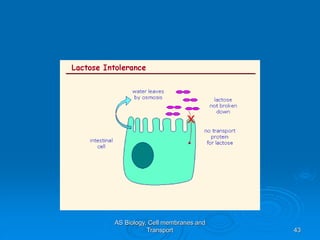
1) Diffusion and facilitated diffusion allow small, nonpolar molecules and ions to passively move across the phospholipid bilayer down their concentration gradients.
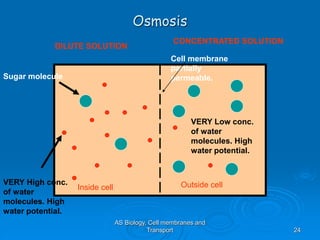
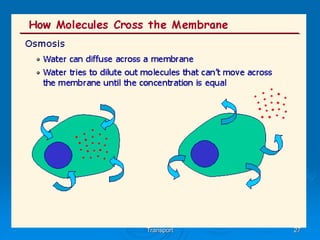
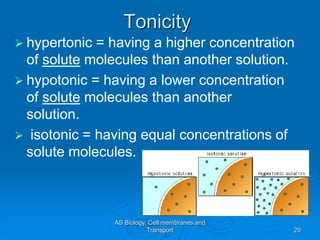
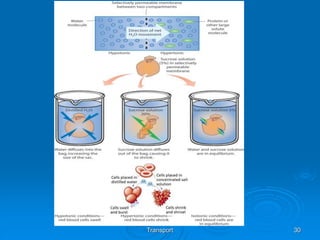
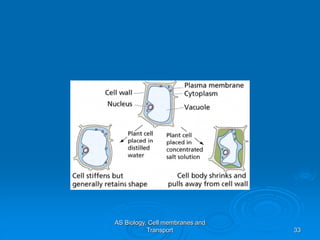
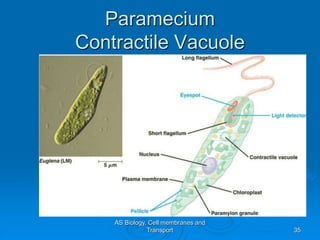
2) Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a partially permeable membrane down its water potential gradient.
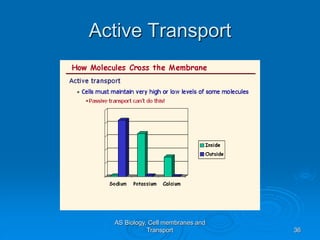
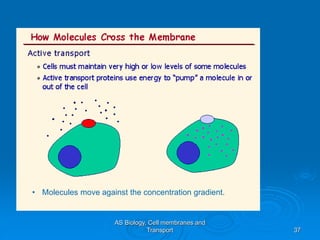
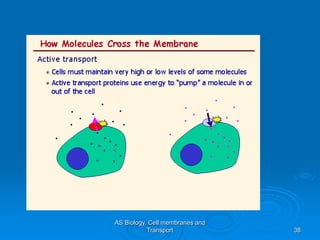
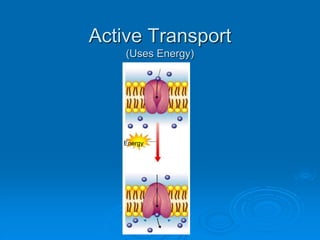
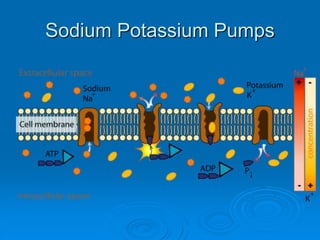
3) Active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradients by using energy in the form of ATP. The sodium-potassium pump is given as an example.
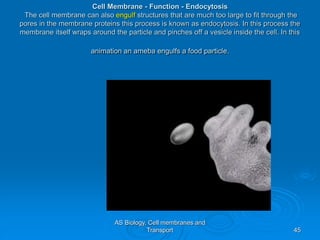
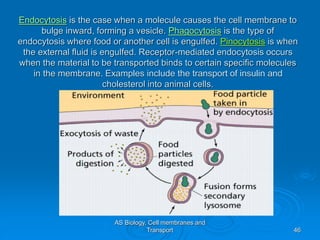
4) Bulk transport involves vesicle-mediated endocytosis and exocytosis to transport larger particles and molecules into and out of cells.