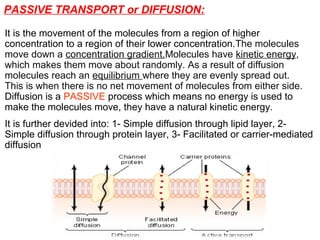
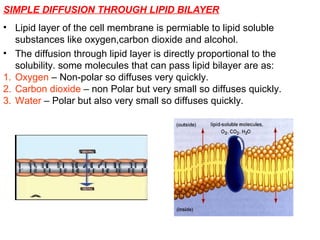
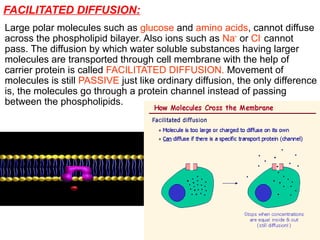
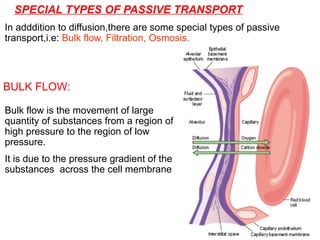
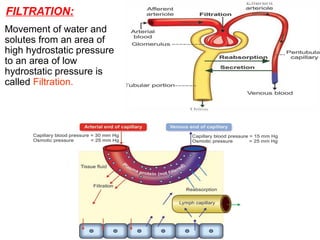
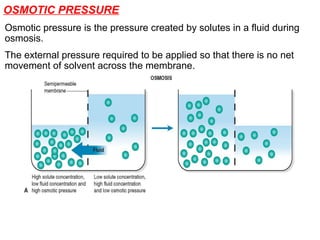
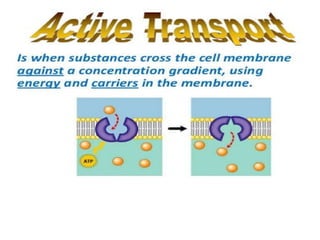
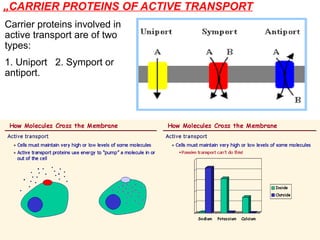
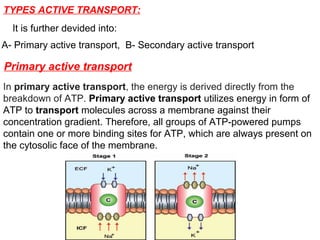
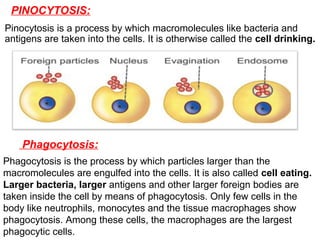
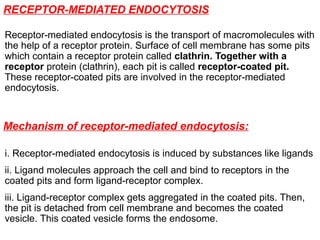
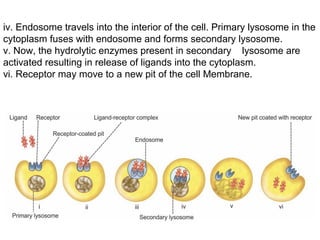
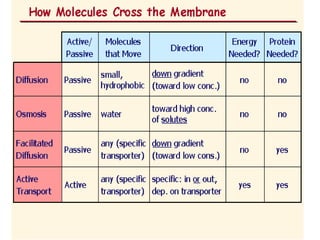
The document discusses the function and mechanisms of the cell membrane, highlighting its selective permeability and the processes of diffusion and active transport. It details types of passive transport, such as simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and filtration, as well as various forms of active transport, including endocytosis and exocytosis. The document further explains the importance of osmotic pressure in biological systems and compares active transport with facilitated diffusion.